DNA and RNA nucleic acid sequences containing consecutive guanine units can form four-stranded structures called G-quadruplexes (G4s). G4s are formed by stacking two or more quartets of guanines (G-quartets). Cancer tissues can contain more G4s than non-malignant cells. The use of small molecules as ligands to bind G4s can modulate their genomic regulatory activity, which can affect the unlimited proliferation typical of cancer cells.
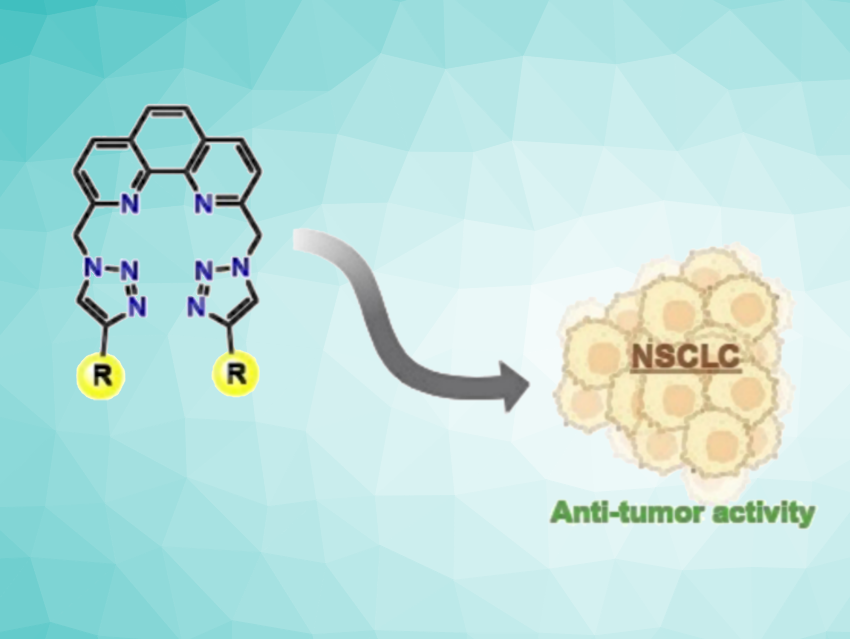
1,10-Phenanthroline derivatives are promising G4 binders, targeting cancer-related G4s. Their structural versatility allows the introduction of different substituents and stereochemical modifications. This can be used for the development of compound libraries for drug development.
Jean-Louis Mergny, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, CNRS, France, Carla Cruz, Universidade da Beira Interior, Covilhã, Portugal, and colleagues have synthesized a series of ten new 1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-bistriazole derivatives using copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reactions. The products contain substituents with different functional groups at the triazole units, e.g., aryl groups, amines or ammonium units, chloro-functionalized alkyl chains, piperazine rings, or morpholine units.
The team evaluated these compounds for their G4 binding and stabilization properties and their anticancer activities. They identified three compounds as promising ligands of the G-quadruplex formed in the KRAS oncogene promoter (KRAS-G4). KRAS is a protein that is overexpressed in various human cancers. While most derivatives showed limited effects on cell viability, a compound with aryl substituents demonstrated cytotoxicity in certain types of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, with minimal impact on the tested non-malignant cells. According to the team, this activity is likely achieved through a mechanism unrelated to the compound’s G4-binding activity. Overall, the work provides new candidates as G4 binding/stabilizing agents and a promising anti-tumor agent.
- Synthesis of 1,10‐Phenanthroline‐2,9‐bistriazoles: Evaluation as G‐Quadruplex Binders and Anti‐Tumor Activity,
Joana Figueiredo, Israel Carreira‐Barral, Pedro Lourenço, André Miranda, Jéssica Lopes‐Nunes, Roberto Quesada, Mafalda Laranjo, Jean‐Louis Mergny, Carla Cruz,
ChemMedChem 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202400591