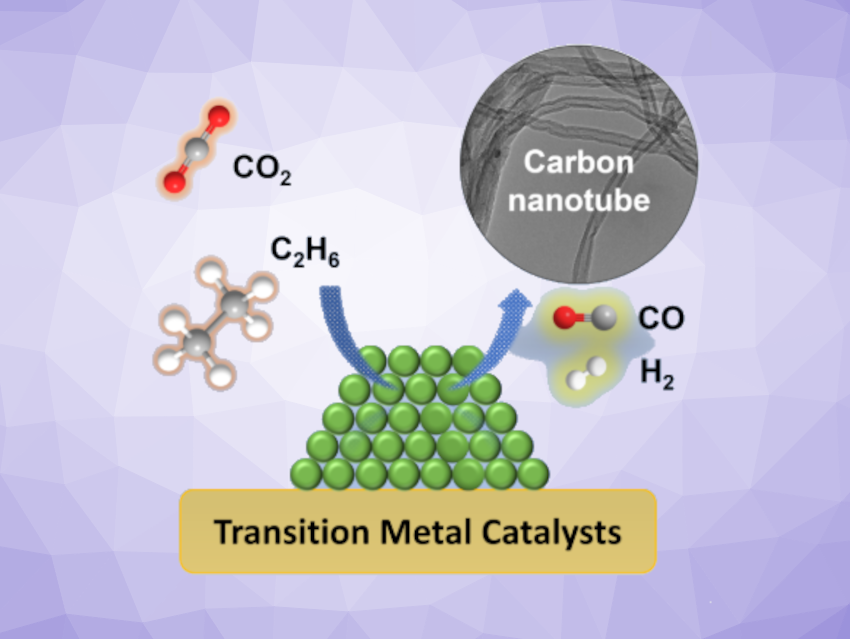
CO2 is a greenhouse gas, but can also serve as a useful chemical building block. The catalytic reduction of CO2 to value-added products could help to improve sustainability. However, using H2 as a reductant can offset the CO2 reduction because it is often produced using fossil fuels. Alkanes could be a useful alternative.
Jingguang G. Chen, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY, USA, and Columbia University, New York, USA, and colleagues have developed a method for transforming CO2 and ethane into carbon nanotubes (CNTs) using earth-abundant metals (Fe, Co, Ni) at 750 °C. The nanotubes are useful products and can serve as long-term carbon storage at the same time.
The team tested different Fe, Co, or Ni-based catalysts and found that Co on an Al2O3 support demonstrated the highest CNT production. CNTs produced using Co or Ni-based catalysts had diameters of ca. 20 nm and lengths in the micrometer range. The process also gives valuable syngas with an adjustable H2/CO ratio.
- Converting Carbon Dioxide into Carbon Nanotubes by Reacting with Ethane,
Yong Yuan, Erwei Huang, Sooyeon Hwang, Ping Liu, Jingguang G. Chen,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202404047
![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)



Useful