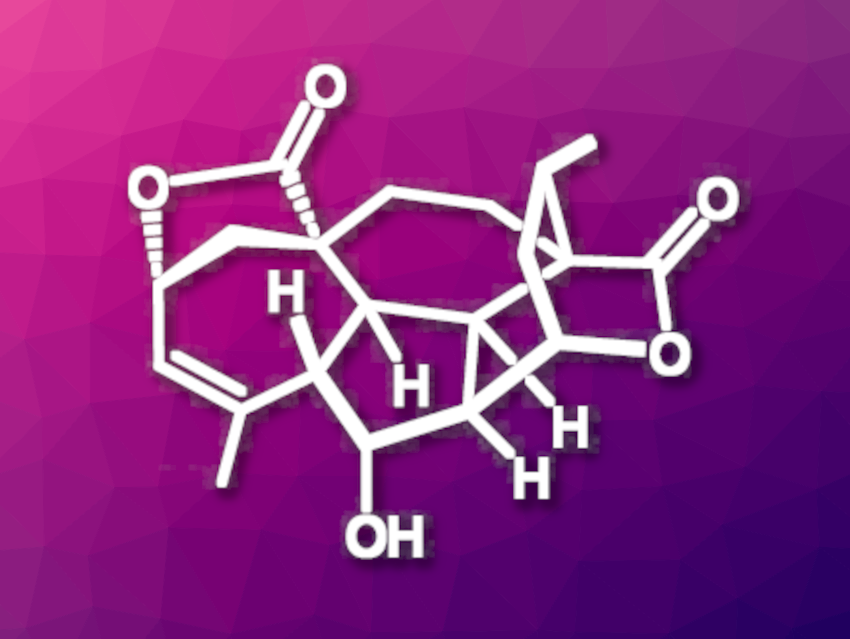
(+)-Mannolide B (pictured) is a diterpene natural product first isolated from a type of yew tree. It has a complex structure with a 5/7/5/6/6/6-fused hexacyclic core, including nine contiguous stereocenters and two quaternary carbon centers. Members of the compound family that includes mannolide B have shown interesting bioactivities. So far, there had been no reported total synthesis of this compound.
Yanxing Jia, Peking University, Beijing, China, and Southwest United Graduate School, Kunming, China, and colleagues have performed the irst total synthesis of (+)-mannolide B. The team started from commercially available (−)-methyl jasmonate (MJA), which is used in the perfume industry. After suitable functionalization of this starting material, the researchers used ring-closing metathesis to close the seven-membered ring of the desired molecular core. The resulting 7/5 bicyclic system was outfitted with a terminal alkyne and converted to a tetracyclic intermediate via a Pauson–Khand-type reaction.
A stereospecific dihydroxylation at the seven-membered ring and a spontaneous lactonization then led to the closing of the fifth ring. The team used a stereoselective Michael addition with vinylmagnesium bromide to obtain a suitable precursor for a Büchner–Curtius–Schlotterbeck reaction that resulted in ring expansion and formed one of the six-membered rings found in the product.
After further functionalization steps used for the construction of the last ring (i.e., the second lactone), the challenging introduction of the vinylmethyl group at C12/C13, and deprotection of the OH group, the team obtained the desired (+)-mannolide B. The analytical data for the synthetic compound was in agreement with that of the natural product. The synthesis was completed in 24 steps starting from (−)-methyl jasmonate.
- Total Synthesis of (+)-Mannolide B,
Peng Chen, Lijun Chen, Hongpeng Lin, Yanxing Jia,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c12767



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)