Silacycles can be useful intermediates in organic synthesis and also have uses, e.g., in pharmaceutical and materials chemistry. The synthesis of silacycles can be achieved, for example, by the transition-metal-catalyzed construction of C–Si bonds in annulation or ring-expansion reactions. However, annulations that involve forming two C–Si bonds between a silicon reagent and an organic substrate are less well studied due to a lack of suitable silicon reagents and limited substrate scopes.
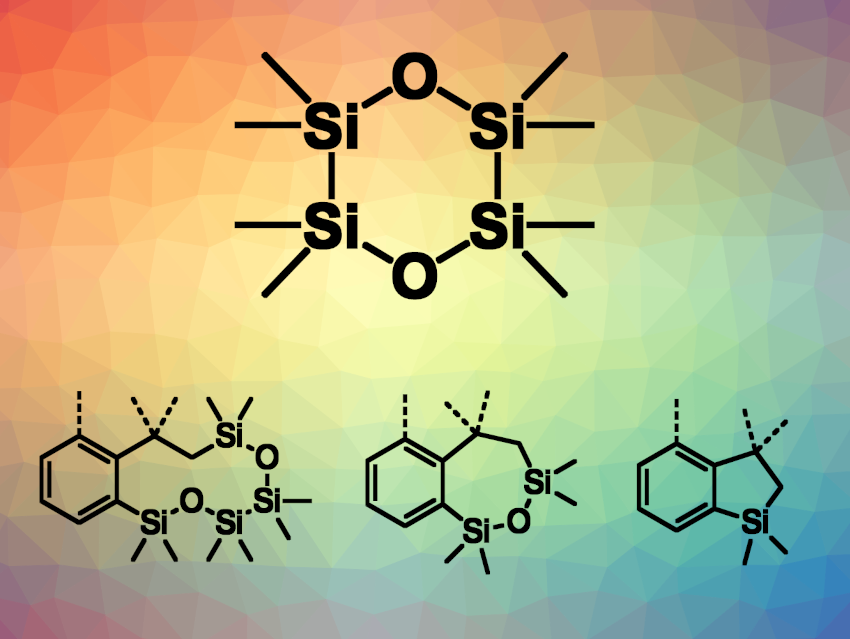
Yun Liang, Yuan Yang, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, and colleagues have used octamethyl-1,4-dioxacyclohexasilane (ODCS, pictured), which can be easily prepared from 1,2-dichlorotetramethyldisilane, as a reagent for the divergent synthesis of silacycles via a time-controlled, palladium-catalyzed reaction (example product structures pictured). The team reacted acrylamide derivatives with ODCS in the presence of Pd(OAc)2 and PPh3, using K2CO3 as a base and dimethylacetamide (DMA) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 100 °C.
The team found that controlling the reaction times enabled the divergent synthesis of silacycles with different ring sizes, including ten-membered rings in benzodioxatetrasilecines, seven-membered rings in benzooxadisilepines, and five-membered rings in benzosiloles. Longer reaction times gave smaller rings. The approach can also be used for the synthesis of ten-, seven-, and five-membered fused silacycles from 2-halo-N-methacryloylbenzamides. The researchers investigated the reaction mechanism and found that the seven- and five-membered silacycles are formed via sequential ring contractions of the ten-membered silacycles.
- Versatile Tetrasilane for Time-Controlled Palladium-Catalyzed Divergent Synthesis of Silacycles via C–H Activation,
Yankun Xu, Mingjie Sun, Weiwei Xu, Guobo Deng, Yun Liang, Yuan Yang,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c02875