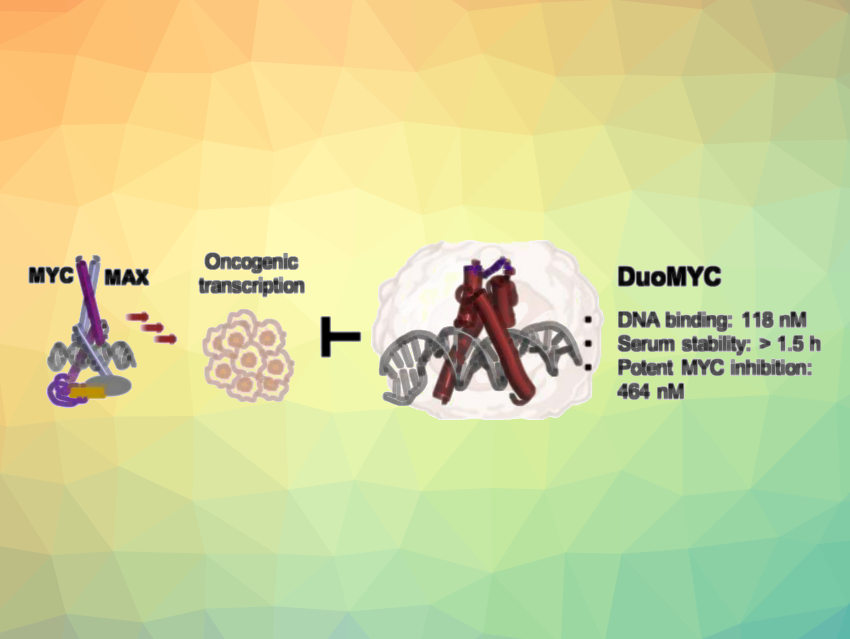
The transcription factor MYC plays a role in over 50 % of all human cancers. It activates gene programs related to cell growth, proliferation, and survival. To achieve this, it heterodimerizes with its “partner” MAX (myc-associated factor X) and as a complex, they bind to a DNA target site called enhancer box (E-Box) to regulate transcription. A MAX/MAX homodimer can also form and act as an inhibitor. In many types of cancer, MYC is overexpressed and disturbs the balance between MYC/MAX and MAX/MAX dimers. This might be interesting for cancer treatment—but MYC is considered an “undruggable” target, with no binding pockets on its DNA binding domain and large intrinsically disordered regions.
Sebastian J. Pomplun, Leiden University, The Netherlands, and Oncode Institute, Utrecht, The Netherlands, and colleagues have developed “DuoMYC”, a synthetic miniprotein that binds to MYC’s target DNA (E-Box) instead of directly to the transcription factor and, thus, can inhibit MYC-driven gene transcription (pictured). The team analyzed the structural features of E-Box-binding proteins and designed a compact dimeric scaffold based on the existing protein-based MYC inhibitor Omomyc, which had been mostly used in research so far due to its limited cell penetration. The researchers essentially aimed to “miniaturize” Omomyc’s structure while retaining the most important features for E-box bonding.
The resulting DuoMYC contains two monomers with 59 residues each, crosslinked using a bis(bromomethyl)biphenyl linker. The team found that DuoMYC binds to E-Box DNA with high affinity, and that it can enter cells and inhibit MYC-driven gene transcription with submicromolar potency. According to the researchers, the miniprotein shows a higher efficacy than several other recently developed MYC inhibitors.
- Development of DuoMYC: a synthetic cell penetrant miniprotein that efficiently inhibits the oncogenic transcription factor MYC,
Brecht D. Ellenbroek, Jan Pascal Kahler, Damiano Arella, Cherina Lin, Willem Jespers, Eliane Ann-Katrin Züger, Micha Drukker, Sebastian J. Pomplun,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202416082