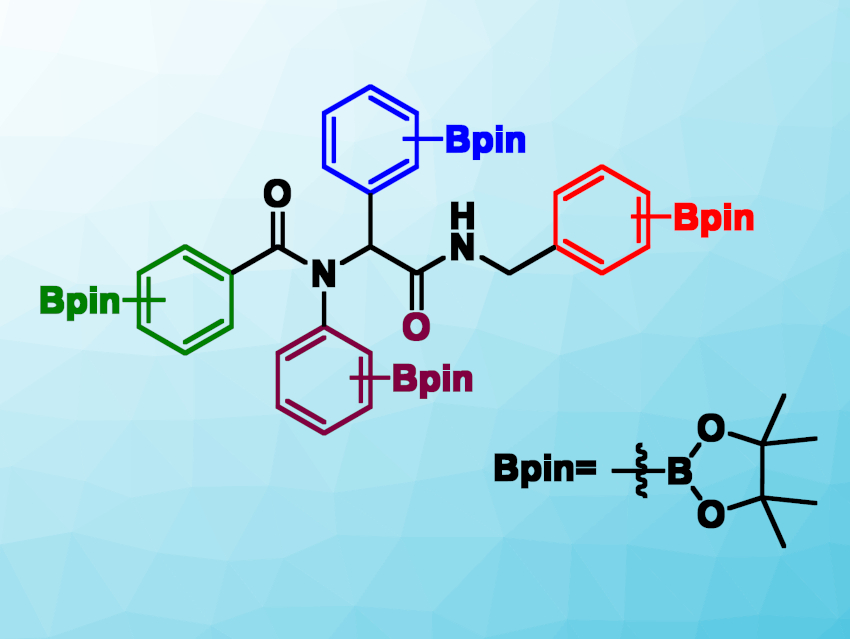
Due to their chemical versatility, organoboron compounds are widely used, e.g., in catalytic reactions, medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, and chemosensors. Diboronic acid compounds, for example, have been used in total synthesis or in the detection of saccharides for diagnostic purposes. Boron compounds can be challenging to synthesize despite their attractive features because they are sensitive to commonly used reagents such as bases, nucleophiles, and oxidants. In addition, the purification of the compounds can be labor-intensive.
Po-Shen Pan, Tamkang University, New Taipei City, Taiwan, and colleagues have synthesized tetraboronate esters (pictured) via a robust microwave-assisted Ugi reaction on a gram-scale in a one-pot process. The Ugi reaction is a four-component reaction that gives a bisamide. The team reacted four boron-containing components: an aldehyde, an amine, a carboxylic acid, and an isocyanide. The reactions were performed under microwave irradiation using 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE) as the solvent.
The desired tetraboronate esters were obtained in moderate to excellent yields. They can be cleanly transformed into the corresponding boronic acids using an oxidative deprotection protocol. The work could provide a user-friendly way to create new functional materials containing multiple boron-based functional groups.
- Robust Synthesis of Tetra‐Boronate Esters Analogues and the Corresponding Boronic Acids Derivatives,
Shuo-Bei Qiu, Jing-Han Xiao, Pin-Rui Chen, Kuan-Lin Ai, Kuan-Lin Pan, Jen-Kun Chen, Yi-Wei Chen, Po-Shen Pan,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202200379