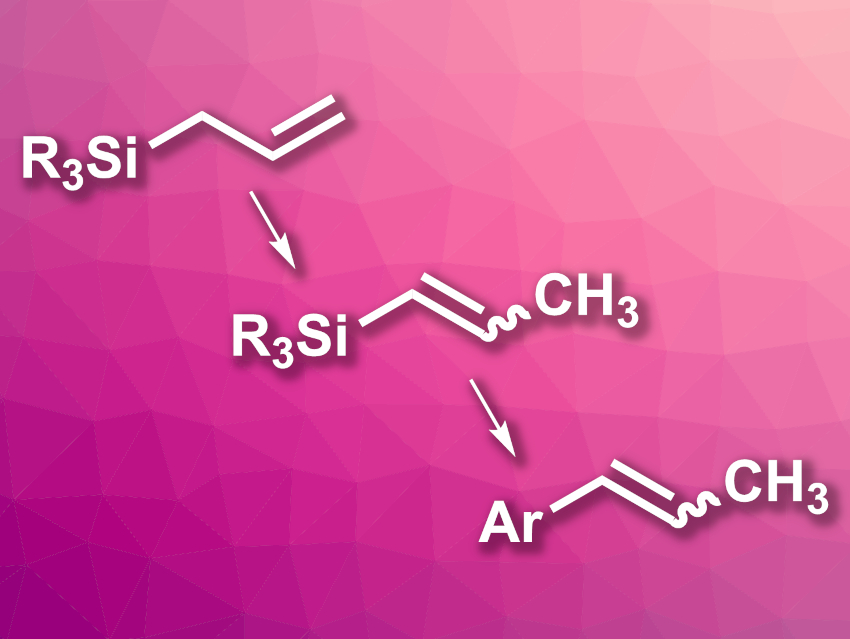
Alkenyl silanes are useful in organic synthesis and can take part e.g., in cross-coupling reactions or polymerizations. One promising path for the synthesis of alkenyl silanes is the isomerization of allyl silanes, which are generally easy to prepare and/or commercially available.
Louis C. Morrill, Cardiff University, UK, and colleagues have developed a one-pot, two-step process in which allyl silanes first undergo an isomerization to alkenyl silanes and then take part in a Hiyama coupling to give styrene derivatives (general reaction sequence pictured). The team started from various aryl- or alkyl-substituted allyl silanes, which were isomerized using B(C6F5)3 as a catalyst and toluene as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 140 °C and gave mostly high yields and good selectivities for the E-isomers.
As a second step, the researchers performed a palladium-catalyzed Hiyama coupling between the resulting prop-1-en-1-yl silanes and a range of different aryl iodides. This second reaction was performed using Pd(dba)2 (dba = dibenzylideneacetone) as a catalyst in the presence of n-Bu4NF at 40 °C. The desired styrenes were obtained in good yields and with high E-selectivities. Overall, the approach provides access to a broad range of styrene derivatives.
- One-Pot Synthesis of Styrene Derivatives from Allyl Silanes via B(C6F5)3-Catalyzed Isomerization–Hiyama Coupling,
Betty A. Kustiana, Rebecca L. Melen, Louis C. Morrill,
Org. Lett. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03584