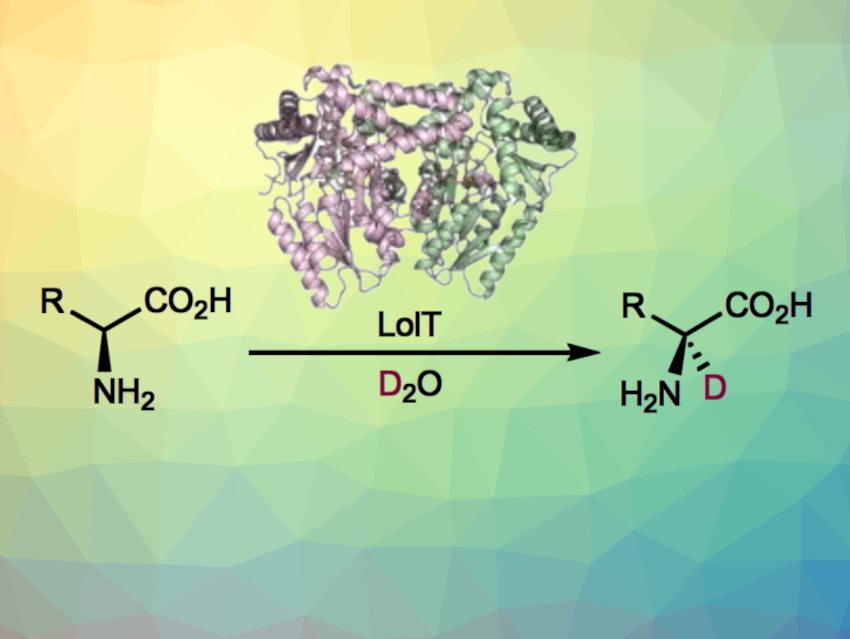
The enzyme LolT, which is dependent on the cofactor pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP), can catalyze Mannich-type cyclizations to give quaternary amino acids (general reaction pictured below). LolT catalyzes a deprotonation of the amino acid substrates to generate α-carbanion intermediates.
Inspired by this mechanism, Yang Hai, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA, and colleagues hypothesized that LolT can catalyze a reversible proton transfer on amino acids that cannot undergo an intramolecular Mannich cyclization reaction. The team prepared a LoIT mutant and tested its deuteration activity in D2O. They found that the enzyme can deuterate a broad range of L-amino acids (general reaction pictured below)—from basic to acidic, nonpolar to polar, and aliphatic to aromatic amino acids with both site- and stereoselectivity.
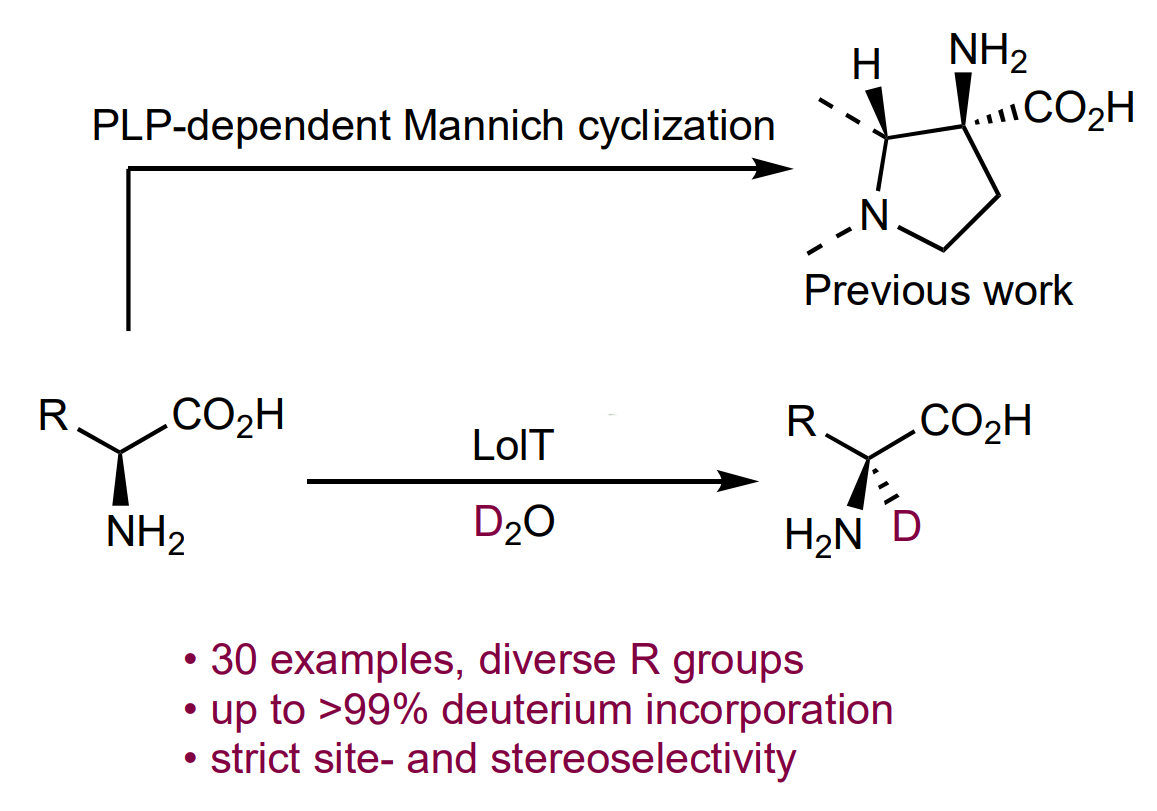
These results suggest LolT is a versatile biocatalyst for L-amino acid α-deuteration. Furthermore, the ability of LolT to generate α-carbanions from a broad range of amino acids could be useful for other applications.
- Stereoselective Biocatalytic α‐Deuteration of L‐Amino Acids by a Pyridoxal 5’‐Phosphate Dependent Mannich Cyclase,
Jinmin Gao, Chen Zhou, Yang Hai,
ChemBioChem 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202300561