Fluoranthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon that consists of a benzene and a naphthalene unit that are fused to form a central five-membered ring. Fluoranthene groups are found, e.g., in natural products or used in fluorescent materials. Existing synthetic paths to fluoranthene derivatives often require harsh conditions and/or have limited substrate scopes.
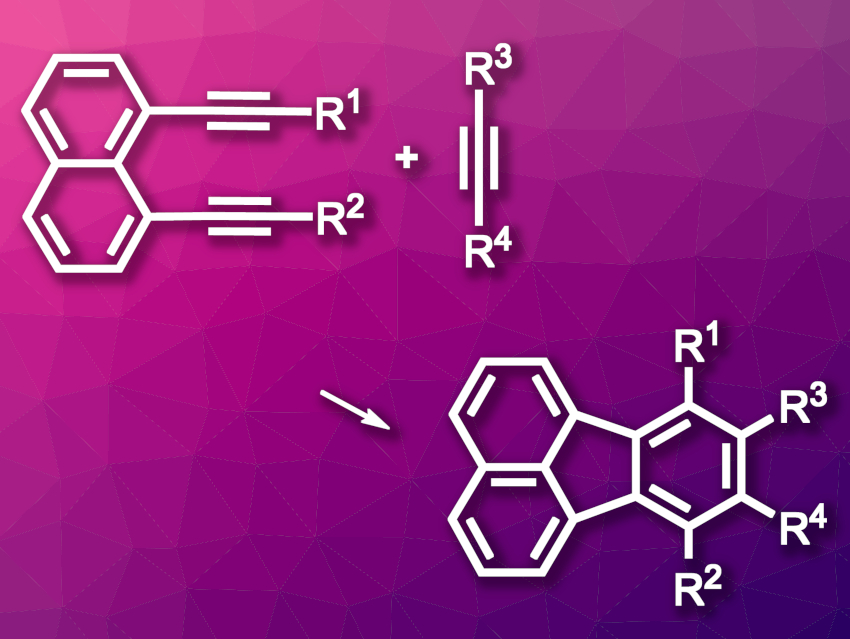
Yuki Nagashima, Ken Tanaka, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, and colleagues have developed a method for the room-temperature synthesis of substituted fluoranthenes and azafluoranthenes (general reaction for fluoranthenes pictured). The team’s strategy is based on a [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition of 1,8-dialkynylnaphthalenes and alkynes. They used [Rh(cod)2]BF4 (cod = 1,5-cyclooctadiene) as the catalyst and H8-BINAP as a ligand to react 1,8-dialkynylnaphthalenes with alkynes, methyl cyanoformate, or isocyanates at room temperature.
The desired fluoranthenes and azafluoranthenes were obtained in good yields. The team used both internal and terminal alkynes. Diphenyl-substituted diynes and diarylacetylenes were found to be particularly well-suited substrates. According to the researchers, the method could be useful for the synthesis of extended π-conjugated molecules.
- Room Temperature Fluoranthene Synthesis through Cationic Rh(I)/H8-BINAP-Catalyzed [2 + 2 + 2] Cycloaddition: Unexpected Acceleration due to Noncovalent Interactions,
Ryota Abe, Yuki Nagashima, Jin Tanaka, Ken Tanaka,
ACS Catal. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.2c05683