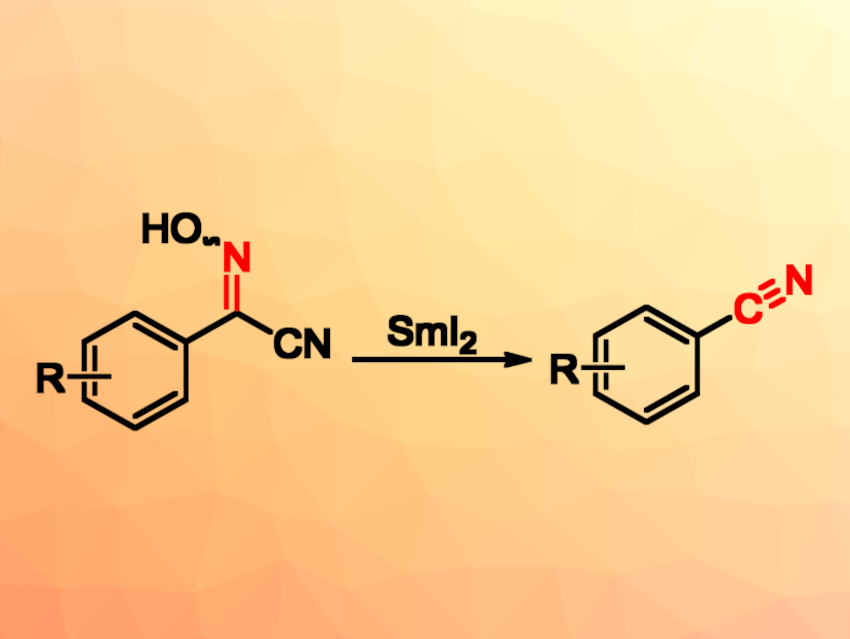
Reactive species such as N-centered radicals and N-centered anions can be useful in organic synthesis. For example, the use of SmI2 for promoting the reductive cleavage of N–O bonds in oxime derivatives is an interesting method for generating such N-active centers. This could be useful, e.g., for the synthesis of aromatic nitriles, which can, in turn, act as precursors for the preparation of aldehydes, amides, amines, etc.
Songlin Zhang, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, and colleagues have developed a method for the reduction of cyanoximes to aromatic nitriles. The team found that the reductive cleavage of N–O bonds in cyanoximes by SmI2 can produce N-centered anions. The in situ-generated N-centered anions can then undergo a C–C bond cleavage to give aromatic nitriles (pictured below). The reactions were performed in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at room temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere within 10 min.
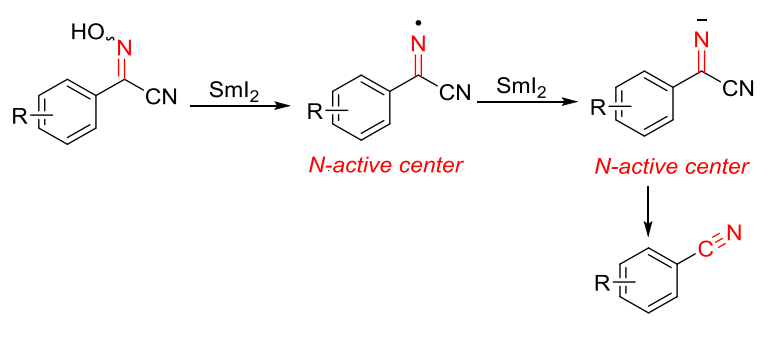
Overall, the work provides a mild, safe, and efficient method for the synthesis of aromatic nitriles in a one-pot manner. The method exhibits good functional-group tolerance, with a broad range of aromatic nitriles obtained in good to excellent yields.
- Synthesis of Aromatic Nitriles by SmI2‐Mediated Reductive Cleavage of Cyanoximes,
Dengbing Xie, Ming Lin, Pengkai Wang, Lingyu Zhang, Songlin Zhang,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202300859