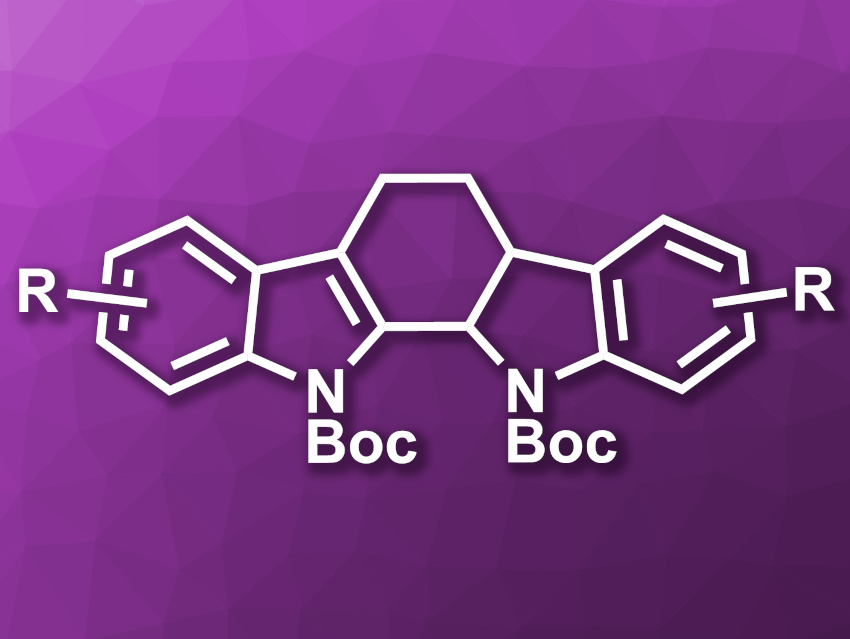
Indolocarbazoles (example pictured above) are bisindole alkaloids. This family of compounds has shown interesting bioactivities and, e.g., includes potential anti-cancer drug candidates. Methods for the synthesis of indolocarbazole alkaloids are, thus, interesting research targets.
Xiaogang Tong, Chengfeng Xia, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, and colleagues have developed a photochemical synthesis of indolocarbazoles from N-allenyl-2-iodoanilines (pictured below). The team used different substituted N-allenyl-2-iodoaniline derivatives as substrates, which were reacted in the presence of [Ir(dFppy)2(dtbbpy)]PF6 (dFppy = 2-(2′,4′-difluorophenyl)pyridine, dtbbpy = di-tert-butylbipyridine) as a photocatalyst and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA), using MeCN as the solvent. The reactions were performed under visible-light irradiation at 50 °C.
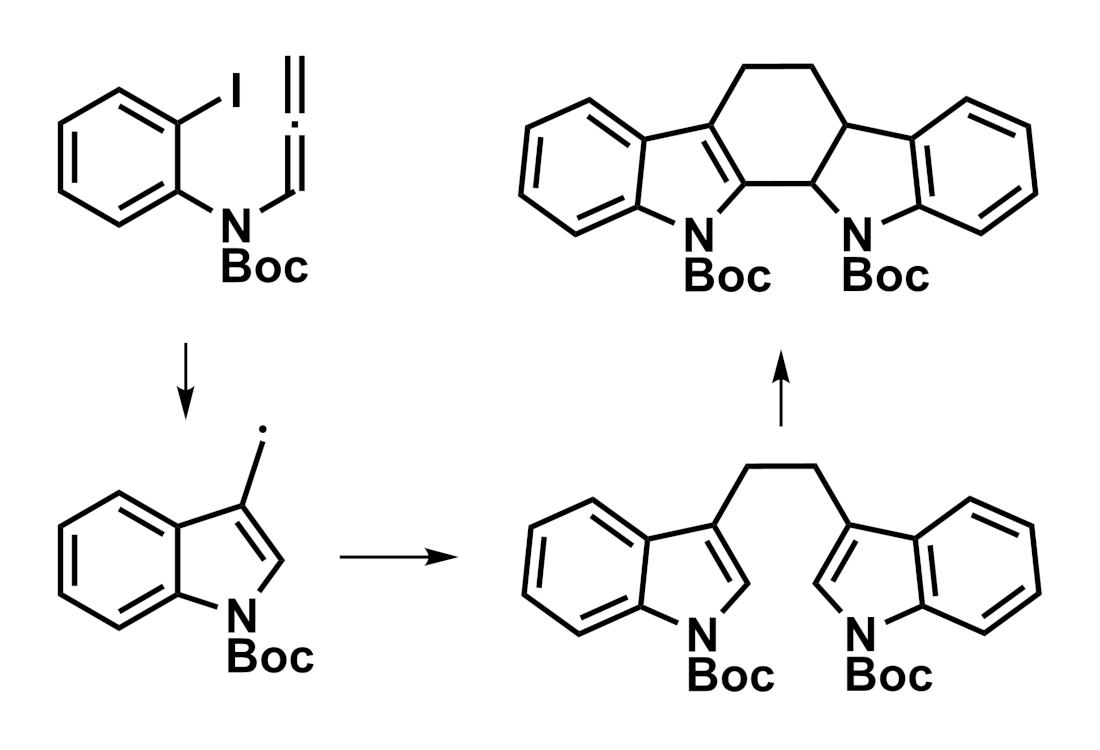
The desired products were obtained in moderate to high yields. The researchers propose a mechanism that proceeds via the formation of a radical from the N-allenyl-2-iodoaniline and an intramolecular 5-exo–trig cyclization to give a 3-methylindole radical intermediate. This intermediate can then dimerize, followed by a Mannich cyclization to give the indolocarbazole product.
- Photochemical Synthesis of Indolocarbazoles through Tandem Indolization/Dimerization/Mannich Cyclization from Allenes,
Jiaying Tang, Linlin Ren, Jianwei Li, Yonggong Wang, Dongyan Hu, Xiaogang Tong, Chengfeng Xia,
Org. Lett. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c01371


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)
