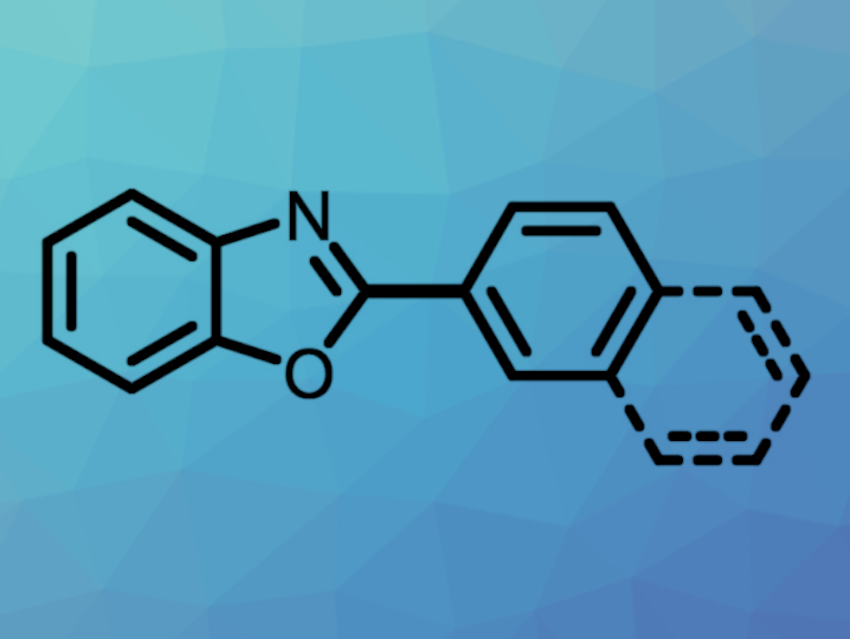
More atom-economical and environmentally benign synthetic methods are interesting research targets to improve sustainability. Approaches for activating C‒O bonds in arenols or aryl ether derivatives, which are abundant in biomass, could be useful in this context.
Tiow-Gan Ong, Academia Sinica and National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC, and Kaohsiung Medical University, Taiwan, ROC, and colleagues have developed a method for a nickel-catalyzed heteroarene C−H/arenol C−OH coupling (pictured below). The reaction overcomes the high energy needed for C‒O bond cleavage and eliminates the need for strong Lewis-acid additives. The team used NiBr2(PPh3)2 as a catalyst together with 1,2-bis-(dicyclohexylphosphino)ethane (dcype) as a ligand, pivalic anhydride (Piv2O) as an in-situ activating agent, and Cs2CO3 as a base. The reactions were performed in 1,4-dioxane at 140 °C.
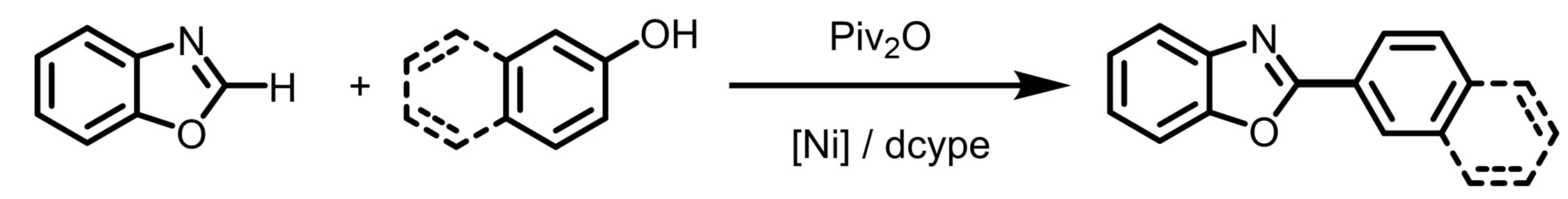
Under these conditions, a variety of oxazole derivatives were coupled with different 2-naphthols. The team proposes that the reaction proceeds via the formation of an aryl pivalate ester from the arenol and the pivalate anhydride, followed by coupling via a catalytic cycle based on Ni(0)/Ni(II) species. A replacement of Piv2O as the activating agent with PhNTf2 also allowed for the use of phenol derivatives as substrates.
- Coupling of Heteroarene and Arenol via Nickel‐Catalyzed C−H/C−OH Activation,
Chen‐Hsun Hung, Ting‐Hsuan Wang, Glenn P. A. Yap, Joon Ching Juan, Tiow‐Gan Ong,
ChemCatChem 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202300249