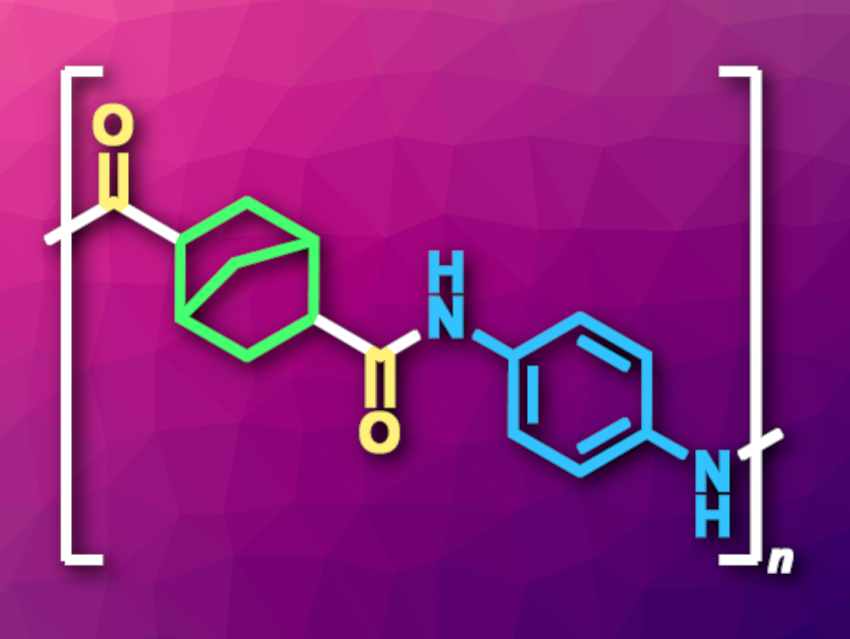
Polyamides are not only found in nature, but synthetic polyamides are also commonly used in, e.g., textiles or materials used in the automotive industry. These polymers are often synthesized via the polycondensation of dicarboxylic acid derivatives with diamines or the ring-opening polymerization of lactams. Complementary methods can be useful, for example, when the corresponding monomers are difficult to access. The palladium-catalyzed carbonylative polymerization of aromatic dihalides, CO, and diamines is one example, but requires stoichiometric amounts of base and suffers from limited atom economy.
Zheng-Hui Guan, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, and colleagues have developed a palladium-catalyzed polymerization of dienes, CO, and diamines that avoids this problem and gives cycloaliphatic semiaromatic polyamides (example pictured). The team reacted dienes such as norbornadiene or cyclohexa-1,4-diene with a variety of aromatic diamines such as p-phenylenediamine or benzidine, as well as CO, using PdI2 as the catalyst together with the diphosphine ligand Xantphos and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as the solvent. The polymerizations were performed at 120 °C.
Under these conditions, the desired polyamides were obtained in mostly high yields and high molecular weights. The reaction tolerates different functional groups, which could be useful in the development of functional polymers. Compared with polyamides made from acyclic adipic acid (hexanedioic acid), the products show higher thermal resistances and improved solubilities, which could make them promising for use in high-performance materials.
- Synthesis of Cycloaliphatic Polyamides via Palladium-Catalyzed Hydroaminocarbonylative Polymerization,
Yaodu Zhang, Fei Wu, Hui-Yi Yang, Gang Wang, Zhi-Hui Ren, Zheng-Hui Guan,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 12883–12888.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c01210