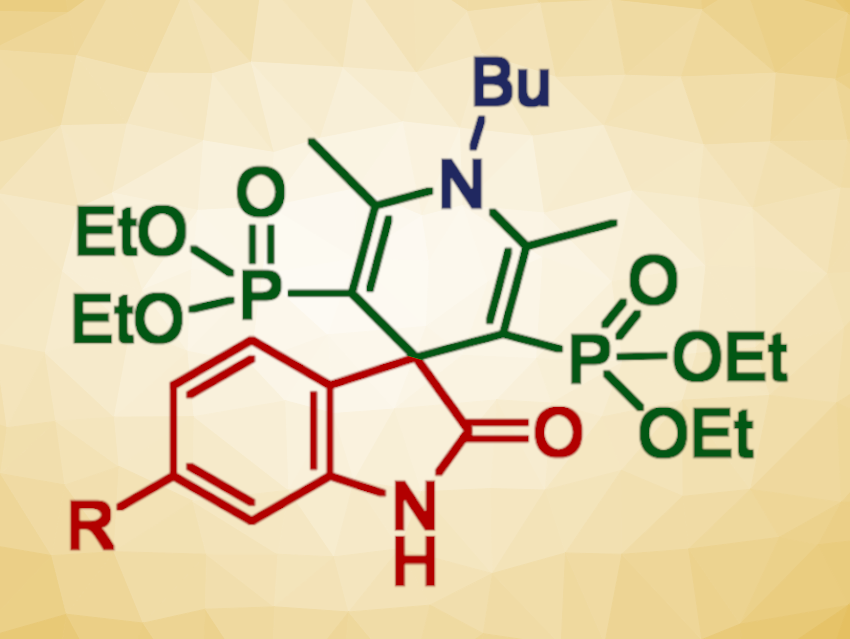
Spirooxindole-containing compounds can show interesting biological activities. 1,4-dihydropyridine units are also often present in pharmaceutically active compounds. Combining both of these structural motifs could, thus, be useful in drug development. It also poses interesting challenges for organic synthesis.
Erika Bálint, Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary, and colleagues have developed a microwave-assisted multicomponent method for the synthesis of spirooxindole dihydropyridine bisphosphonates (example structure pictured). The synthesis uses isatins, β-ketophosphonates, and primary amines as the building blocks in a one-pot, catalyst- and solvent-free reaction. The reactions were performed using two equivalents of the respective β-ketophosphonate at 120 °C under microwave irradiation.
Under these conditions, the desired spirooxindole derivatives, representing a new family of compounds, were obtained in mostly moderate to good yields. The team obtained 19 examples of new spirooxindole dihydropyridine bisphosphonates. According to the researchers, the developed method may be a useful synthetic tool due to the prevalence of the products’ key subunits in natural products and biologically active molecules.
- Microwave‐assisted multicomponent synthesis of spirooxindole dihydropyridine bisphosphonates,
Bettina Rávai, Áron Soma Németh, Zsolt Kelemen, Erika Bálint,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202400873