Bioisosteres are valuable design elements for medicinal chemists, allowing modification of structural and pharmacokinetic properties to optimize bioactive compounds as drug candidates. Thioamides show potential as effective bioisosteres for widely used amide pharmacophores.
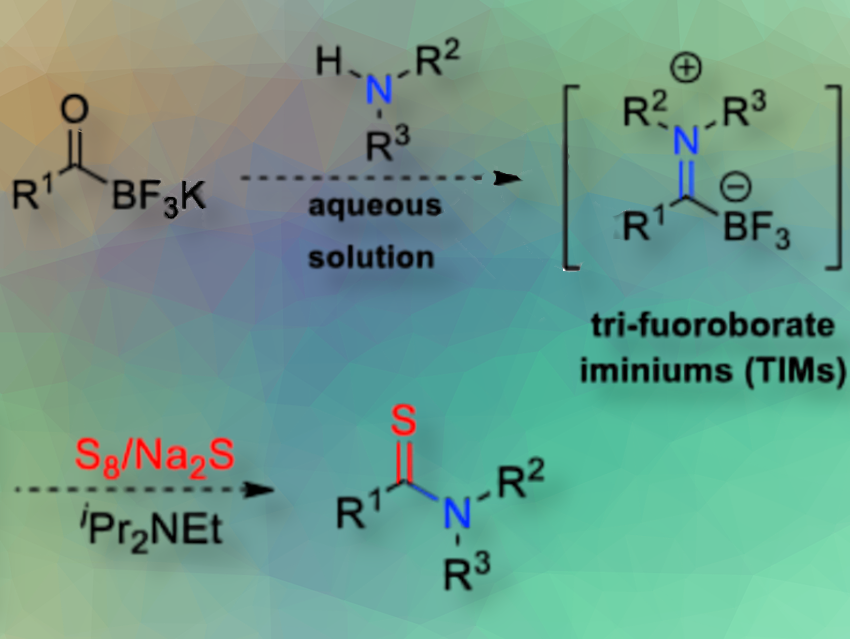
Jing Li and colleagues, Xi’an Jiaotong University, China, have developed a synthesis method for thioamides, achieved through the reaction of potassium acyltrifluoroborates (KATs) with amines in the presence of elemental sulfur in aqueous solution. The process is simple, mild, and accommodates various polar functional groups, making it ideal for creating amide and thioamide drug libraries.
The reaction begins with the acid-mediated formation of trifluoroborate iminium salts (TIMs) from KATs and amines (pictured above). In the presence of Na₂S and elemental sulfur, reactive polysulfide species are generated, which subsequently react with the TIM intermediates to afford thioamides under mild, aqueous THF/H₂O conditions. Diisopropylethylamine (iPr₂NEt) serves as a base that, when combined with Na₂S, significantly enhances thioamide formation.
Furthermore, the team has synthesized seven bioactive thioamides and their corresponding marketed drug analogs using this method, including thioamide analogs of Tritiozine (an antisecretory agent), Tracimine (an antidepressant), a D3 dopamine receptor agonist (used in neurological disorders), Biltricide (an anthelmintic), ciprofloxacin (an antibacterial agent), and Elesclomol (investigated for cancer treatment).
- Chemoselective thioamidation of potassium acyltrifluoroborates (KATs) and amines using elemental sulfur in aqueous solution,
Yuanhang Li, Hafiza Zara Tariq, Silong Xu, Jing Li,
Eur. J. Org.Chem. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202500330