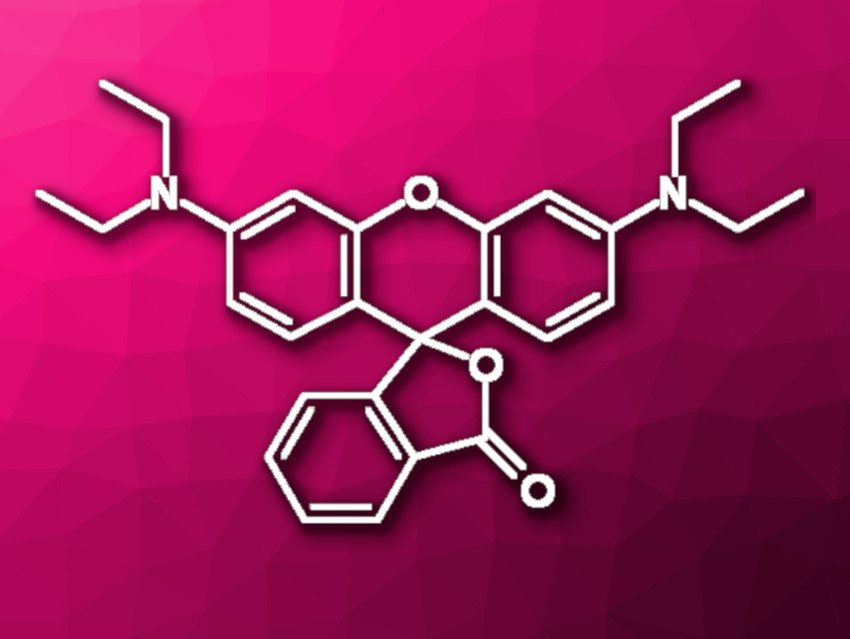
Rhodamine B (pictured) is a fluorescent dye with a xanthene core. Rhodamine derivatives can be used, e.g., as a fluorescence standard in analytical methods, in bioimaging, as a laser dye, or in organic LEDs (OLEDs). Due to the wide range of applications of this type of dye, sustainable methods for the synthesis of rhodamines are interesting research targets.
Amol A. Kulkarni, CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India, and Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research (AcSIR), Ghaziabad, India, and colleagues have developed a simple, catalyst- and solvent-free protocol for the continuous flow synthesis of rhodamine B dyes that uses a mechanochemical approach with a single screw reactor. The team reacted 3-dialkylamino phenols with phthalic anhydride derivatives at 180 °C. They used a single polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) screw in a glass jacket as the reactor, with a 0.25 mm gap between the glass wall and the screw threads.
Under these conditions, the reaction achieved good yields (70–84 %) within 10–12 min. The researchers prepared six different rhodamine derivatives using this approach. Overall, the developed method is attractive due to its fast reaction times, solvent-free nature, scalability, and operational simplicity.
- Continuous flow solvent-free and catalyst-free mechanochemical production of rhodamine B dyes and their derivatives,
Mukesh Purohit, Tabrez Rafique Shaikh, Amol A. Kulkarni,
Chem. Commun. 2025.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4CC04197F