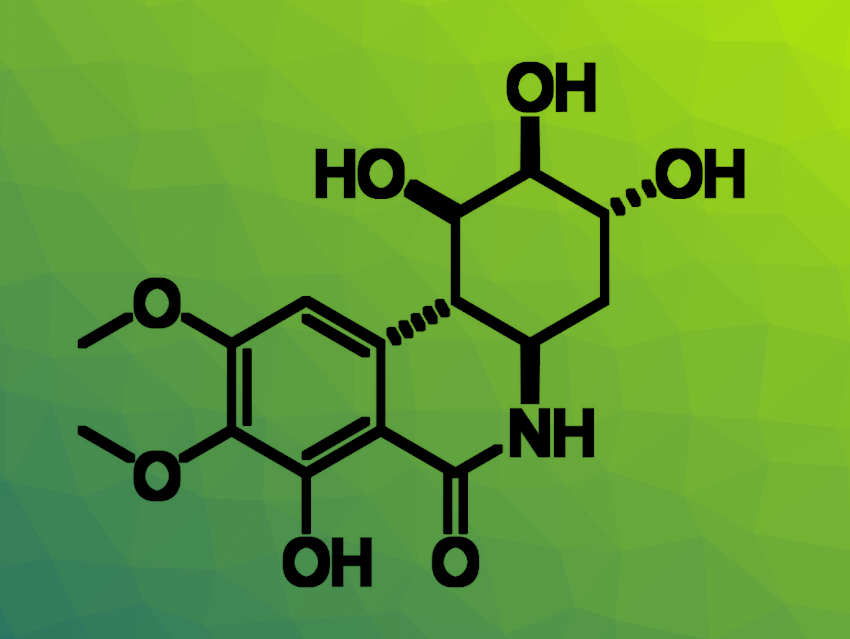
The natural products pancratistatin (pictured below) and narciclasine, found in the family of flowering plants that includes daffodils and snowdrops, have shown biological activities against various diseases. For example, they display anticancer activities—including against certain brain tumors that generally lead to a poor prognosis with current treatment options. Some derivatives of these natural products, which feature a saturated C-ring with three hydroxyl groups, have shown potent biological activities. The commercially available natural product (−)-shikimic acid has three hydroxyl groups and could be used as a building block to form such a C-ring.
Due to the therapeutic potential and the limited supply of natural products like pancratistatin, Lorenzo Caggiano, University of Bath, UK, and colleagues have explored the synthesis of a pancratistatin derivative made from (−)-shikimic acid. Using a Heck reaction and subsequent cyclization, the team first synthesized an unfunctionalized model core of pancratistatin from 1-cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid (as a simpler analogue of shikimic acid) in just two steps and 50 % yield.
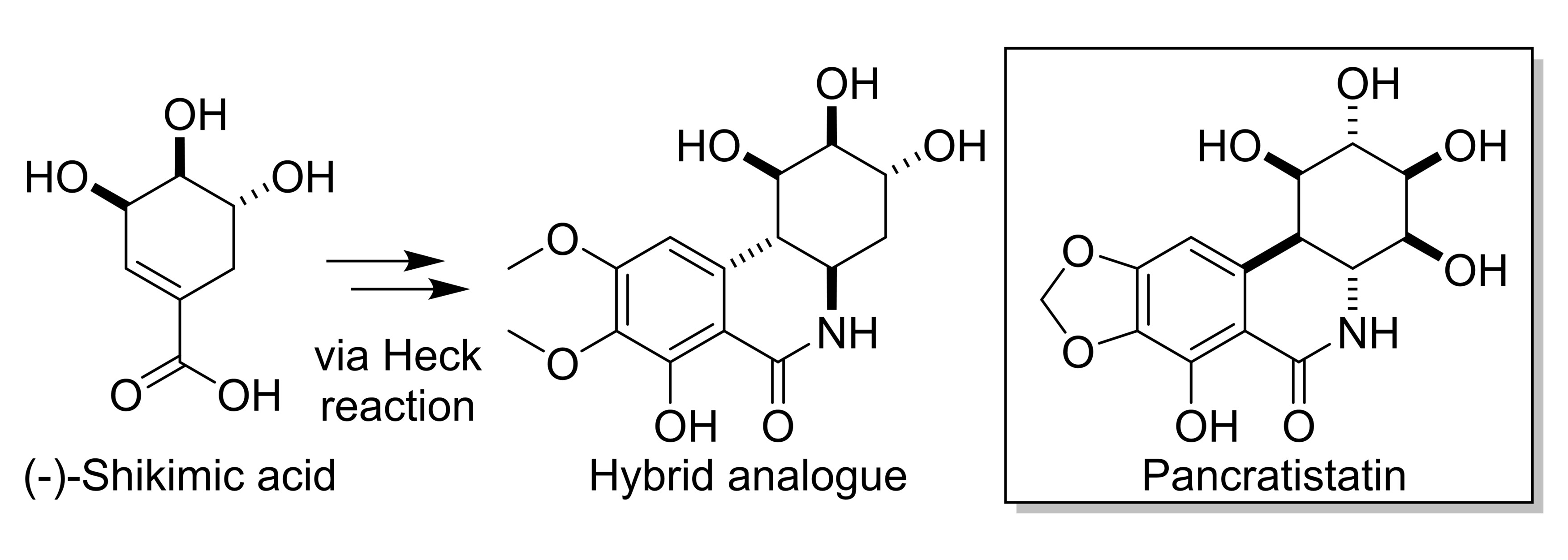
Using an adapted route, also involving a Heck reaction and a cyclization as the key steps, the researchers then synthesized a functionalized hybrid analogue of pancratistatin derived from (−)-shikimic acid (pictured above). The work could allow the exploration of the biological activity of these novel hybrid analogues. According to the team, the route could also be modified to generate tetra-substituted derivatives, as observed in pancratistatin.
- Total Synthesis of a Pancratistatin/Shikimic Acid Hybrid Analogue,
Darlington Azubuike, Gemma A. Di Iulio, Lorenzo Caggiano,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202301247