Chemotherapy drugs against cancer generally have cytotoxic effects that kill cancer cells directly, but their mode of action can also involve eliciting immune effects against tumors. So-called immunogenic cell death (ICD) exploits the host immune system against tumor cells as a “second hit”. Half-sandwich ruthenium complexes have received research attention as potential antitumor agents. However, work on these complexes as inducers of ICD is limited.
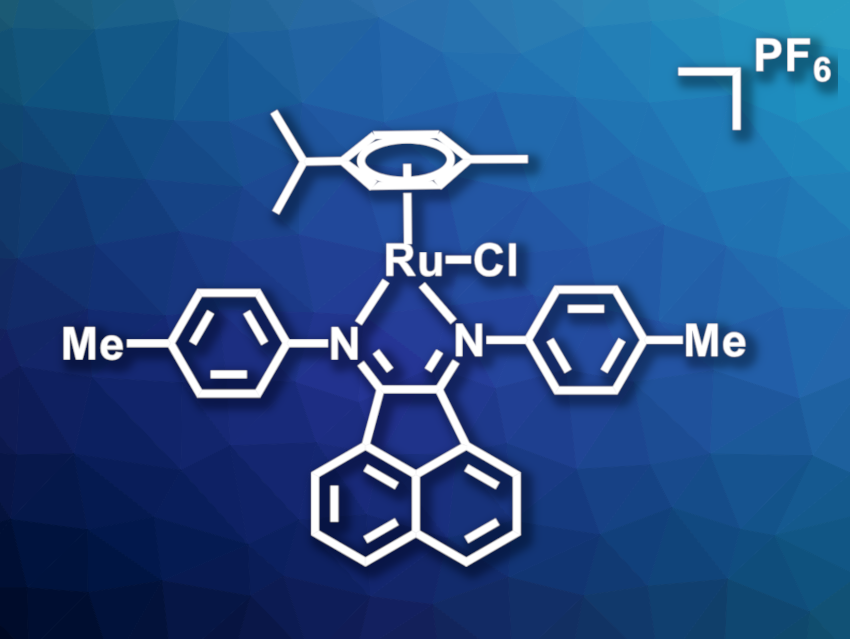
Xiangfeng Song, Xinxiang Medical University, China, Zhe Liu, Qufu Normal University, China, and colleagues have developed a RuII half-sandwich complex that could act as an ICD inducer in melanoma treatment. The complex was obtained via a direct reaction of the dimer [(η6–p-cymene)RuCl2]2 with the chelating ligand aryl-bis(imino)acenaphthene in toluene. The resulting half-sandwich RuII complex was isolated as the PF6– salt (pictured).
The team found that the complex can elicit melanoma ICD in vitro and in vivo (in mice). They also investigated the possible mechanisms of action and found that ICD was associated with mitochondrial damage, stress on the endoplasmic reticulum (a cell organelle with multiple functions), and impairment of metabolic status in melanoma cells. Overall, the work could help with the help to design of new half-sandwich Ru-based organometallic complexes with immunomodulatory properties for melanoma treatment.
- A Half‐sandwich Ru(II) (N^N) Complex: Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death of Melanoma In vitro and In vivo,
Zhishan Xu, Mengke Xu, Xueya Wu, Sheng Guo, Zhongwei Tian, Di Zhu, Jixuan Yang, Jiyun Fu, Xi Li, Guozhen Song, Zhe Liu, Xiangfeng Song,
ChemMedChem 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202300131