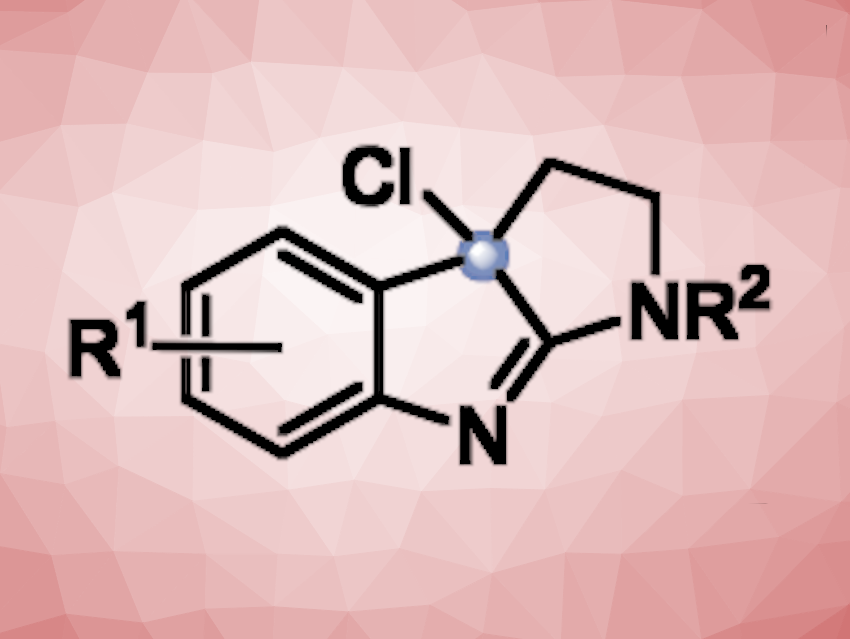
Tryptamine is composed of an indole unit and a 2-aminoethyl group. Tryptamine derivatives can have useful biological activities and are often used in pharmaceutical chemistry. Methods for the functionalization of tryptamines can, thus, be useful in drug development. Late-stage functionalizations can be particularly interesting because they make it easier to build compound libraries from a common precursor.
Qinying Liu, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China, Yu Gao, Haijun Chen, Fuzhou University, China, and colleagues have developed an approach to the late-stage functionalization of tryptamines that uses an inexpensive 10 % NaClO solution in water for an oxidative halocyclization (pictured below on the left). The resulting intermediates can be further functionalized using a variety of different nucleophiles.
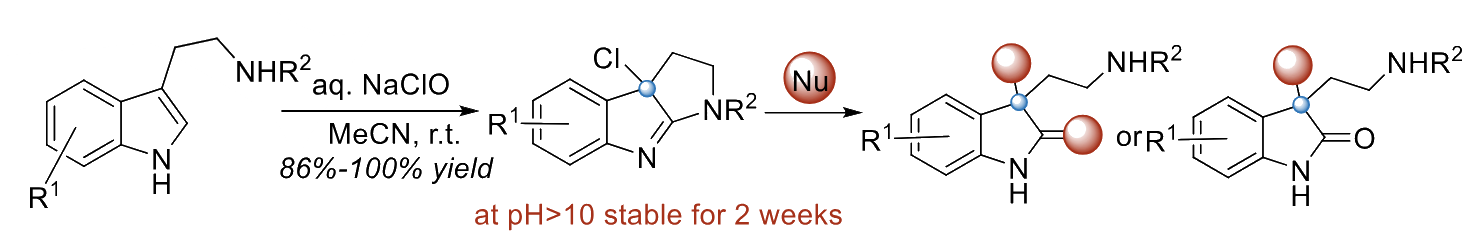
The team reacted a range of tryptamines and 1H-indole-3-propylamines with 4 eq of NaOCl, using acetonitrile as the solvent. The reactions were performed at room temperature, and the desired products were obtained in good to excellent yields.
The products could be further reacted with nucleophiles such as as aromatic amines or alkylamines, and could also be coupled with, e.g., phenols or indoles under acidic conditions. The team found that the oxidative halocyclization reaction can be scaled up to the gram scale and the NaOCl solution can be replaced with commonly available household bleach with little change in yield.
- Green Late‐Stage Functionalization of Tryptamines,
Jiayi Xu, Yahui Zhang, Qiling Cai, Li Chen, Yang Sun, Qinying Liu, Yu Gao, Haijun Chen,
Chem. Eur. J. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202401436