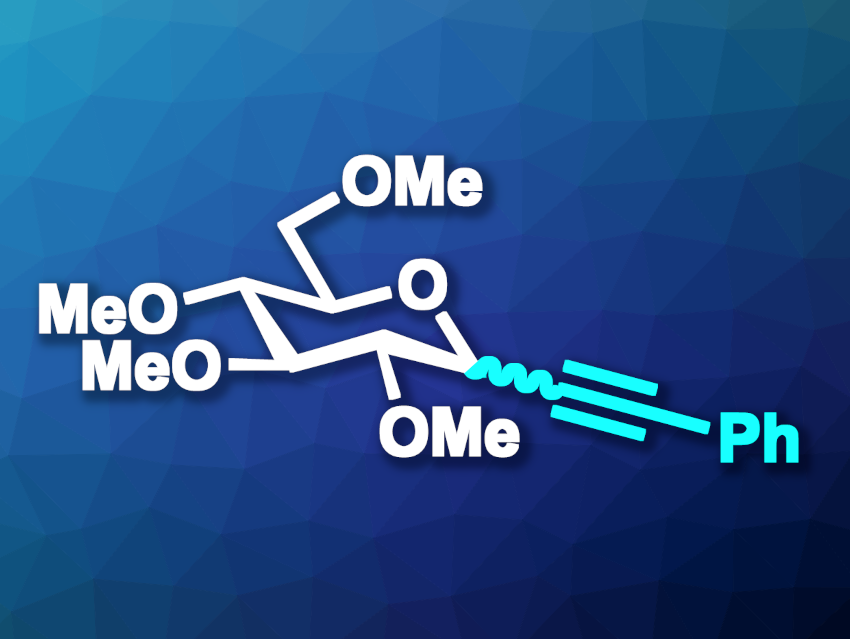
In glycosides, a sugar is bound to another group via a glycosidic bond. O-Glycosides are very common. C-Glycosyl compounds, in which the group is directly connected to the anomeric carbon, can be useful because they are less susceptible to hydrolytic enzymes and can show interesting bioactivities. Alkynyl C-glycosides, for example, can be useful precursors for complex C-glycosides, but synthetic approaches to this type of compound are limited.
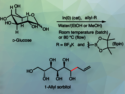
Vincent Dalla, Université Le Havre Normandie, France, Patrick Pale, Jean-Marc Weibel, Université de Strasbourg, CNRS, France, and colleagues have developed a gold(I)-catalyzed, silyl-assisted, α-selective method for the formation of alkynyl C-glycosides (example product pictured). The team reacted different protected acetyl-functionalized sugars with a range of 1-silylated alkynes, using (p-CF3Ph)3PAuOTf (TfO– = triflate) as the catalyst and 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 80 °C.
Under these conditions, the desired alkynyl C-glycosides were obtained in moderate to high yields and with mostly very high α-selectivities. The method was used for both pyranoses and furanoses, with the reaction temperature lowered to 50 °C for the latter. The team proposes a mechanism that involves the formation of a gold acetylide intermediate, which undergoes a nucleophilic addition to the glycoside’s anomeric position. They also state that the work could possibly be extended to other silanes.
- Gold(I)-Catalyzed Access to 1-Alkynyl C-Glycosides from 1-Silylated Alkynes: An Alternative Paradigm for the Direct and α-Stereoselective Alkynylation of Glycosides,
Eliot Starck, Mathieu Pascaretti, Catherine Taillier, Aurélien Blanc, Vincent Dalla, Patrick Pale, Jean-Marc Weibel,
ACS Catalysis 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.4c04293