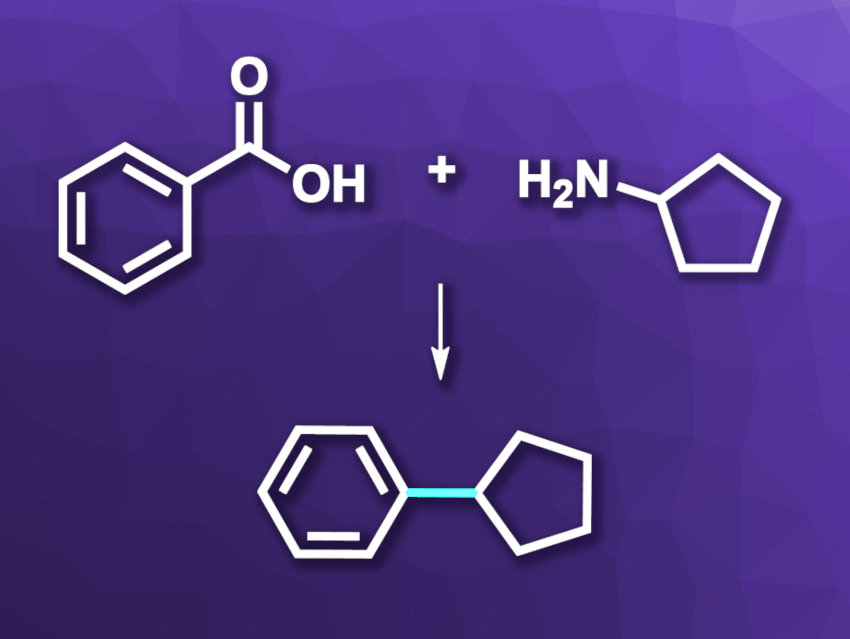
Amines and carboxylic acids are commonly used building blocks in organic synthesis. Usually, they are connected via an amide bond. Using these abundant chemical feedstocks in another way, i.e., in C–C coupling reactions, could further expand their utility. Reductive C(sp3)–C(sp2) coupling reactions, for example, can be performed using nickel catalysis and give useful products.
Tim Cernak, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA, and colleagues have developed a formal cross-coupling of alkyl amines and aryl carboxylic acids to form new C(sp3)–C(sp2) bonds (example reaction pictured). To achieve this transformation, the amine and the carboxylic acid building blocks were activated as pyridinium salts and N-acyl-glutarimides, respectively. This was then followed by a nickel-catalyzed reductive cross-coupling to obtain the desired product.
The conditions for the cross-coupling were optimized using high-throughput experimentation. The team used NiBr2·DME as a catalyst together with 5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine or 5,5′-bis(trifluoromethyl)-2,2′-bipyridine as a ligand, Mn as a reductant, phthalimide as an additive (as well as RuCl3 and GaCl3 in some cases), and NMP (N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 80 °C and can be used, e.g., for the diversification of pharmaceutically active compounds that contain amines or carboxylic acid groups.
- Formal Cross-Coupling of Amines and Carboxylic Acids to Form sp3–sp2 Carbon–Carbon Bonds,
James L. Douthwaite, Ruheng Zhao, Eunjae Shim, Babak Mahjour, Paul M. Zimmerman, Tim Cernak,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c11563