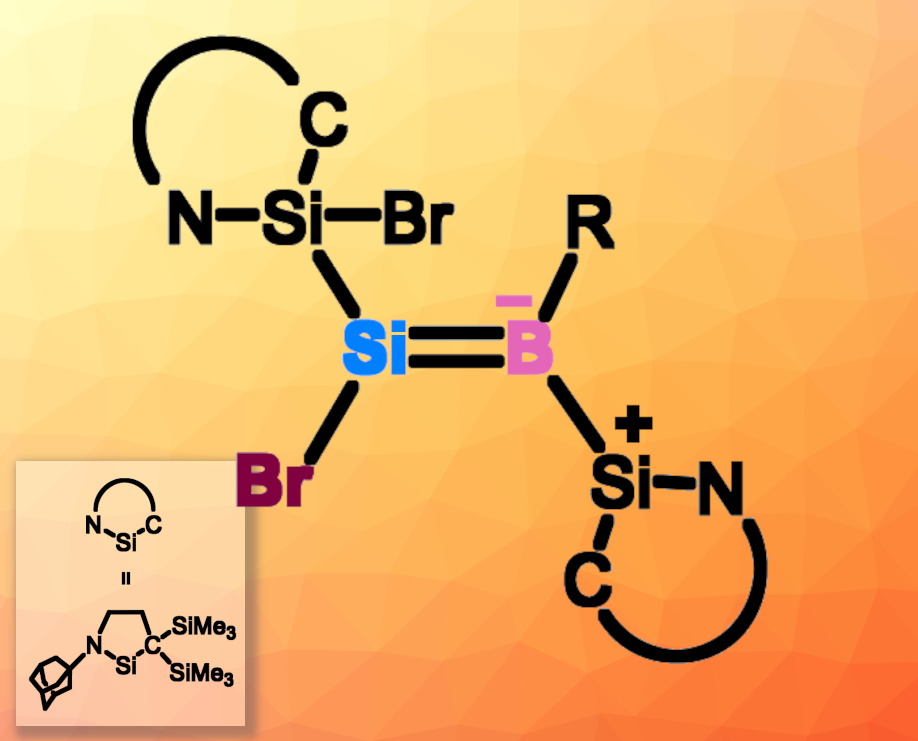
Compounds containing Si–B single bonds, or borylsilanes, can be useful reagents for silylation or borylation reactions. They can also be interesting, e.g., in small-molecule activation. In comparison, less is known about the chemistry of compounds containing Si=B double bonds, such as borasilenes (R2Si=BR) and boratasilenes (R2Si=B−R2).
Takeaki Iwamoto, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, and colleagues aimed to develop a new strategy to form Si=B double bonds. They reacted a silylone that has two cyclic (alkyl)(amino)silylene (CAASi) groups (CAASi2Si:) with dibromomesitylborane (MesBBr2). They obtained the first isolable Si=B analogue of a vinyl halide, a bromoboratasilene (pictured). The structure of the product was confirmed using multinuclear NMR spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectrometry, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The team proposes that the reaction starts with a 1,2-bromoborylation of the silylone, followed by a second 1,2-bromoborylation and silyl and bromo migration. The reaction also gave traces of a borasilacycle, which could be formed via an intramolecular C–H insertion after the second 1,2-bromoborylation step.
The product could be further transformed, e.g., by a reaction with hypersilylpotassium [(Me3Si)3SiK], which gave a potassium 2-borata-1,3-disilacyclopropene and KBr. Not only the Br substituent can serve as a reactive site; the silylene unit can also undergo further reactions, e.g., by coordinating an N-heterocyclic carbene at the Si center. According to the researchers, the developed approach could also be applicable to other zero-valent main-group element-centered complexes and provide access to other types of double bonds between two different elements.
- Isolable Si=B Analogue of a Vinyl Halide: A Building Block for Facile Access toward Silicon‐Boron Multiple Bonded Species,
Taichi Koike, Naoki Sakurata, Shintaro Ishida, Takeaki Iwamoto,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202411283