Phenolic compounds are useful, e.g., in drug discovery. The conversion of boronic acids to the corresponding phenols is appealing since many building blocks based on boronic acids are available. Arylboronic acids can be converted into the corresponding phenols by reactions with, for example, alkaline hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen, N-oxides, or hypervalent iodine compounds.
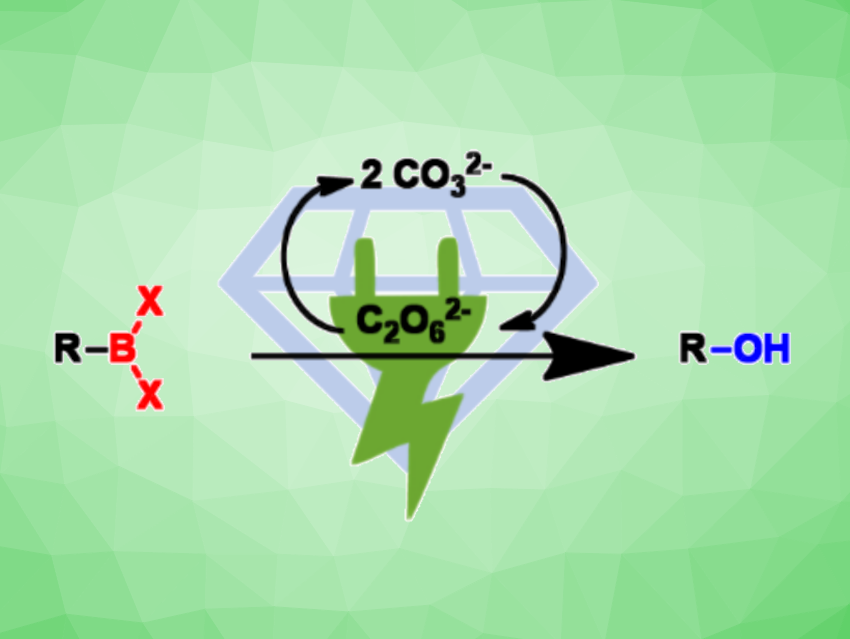
Instead of using hydrogen peroxide/base mixtures, carbonate solutions can be electrolyzed, generating peroxodicarbonate (C2O62–) as a useful alternative oxidizer. Siegfried R. Waldvogel, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany, and colleagues have developed a path to phenols starting from various boronic acids (pictured). The peroxodicarbonate was anodically formed from carbonate at boron-doped diamond electrodes in a flow electrolysis cell. This “green” oxidizer is then added to the boronic acid in ethanol as an environmentally friendly, non-toxic solvent.
The desired products were obtained in high yields (up to 99 %). The conversion can be conducted on a multi-gram scale. Peroxodicarbonate can also be employed in hydroboration/oxidation sequences, leading from alkenes to alcohols. The peroxodicarbonate can be prepared as needed, and no precautions for the storage of dangerous peroxides are required.
- The Oxidation of Organo‐Boron Compounds Using Electrochemically Generated Peroxodicarbonate,
Philipp J. Kohlpaintner, Lucas Marquart, Lukas J. Gooßen, Siegfried R. Waldvogel,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202300220


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)
