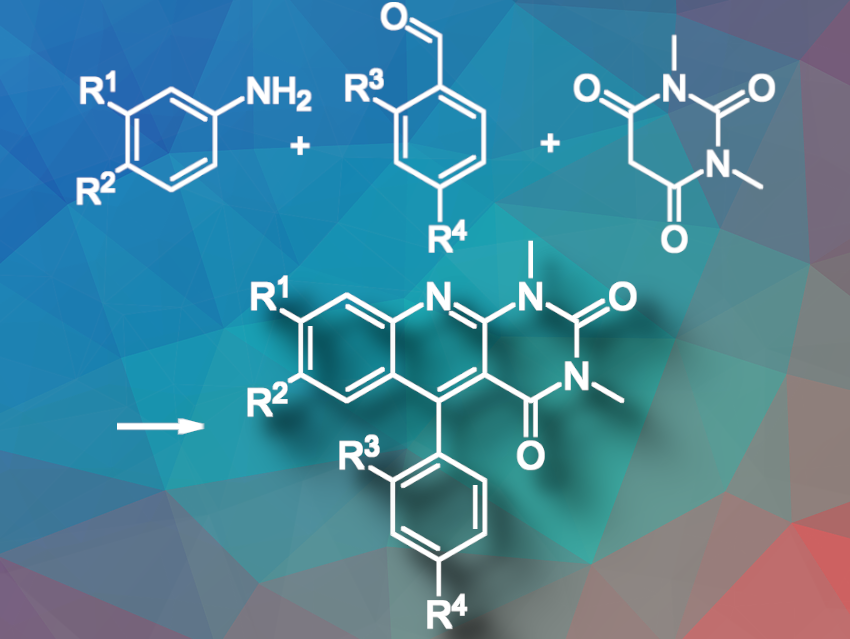
The synthesis of 5-aryldeazaalloxazines has gained interest due to their unique properties, e.g., as powerful reductive photocatalysts. However, current methods do not efficiently introduce an aryl group at C(5) of deazaalloxazines, which confers unique chemical and physical properties on 5-aryldeazaalloxazines.
Tetiana Pavlovska, Ivana Weisheitelová, and Radek Cibulka, University of Chemistry and Technology, Prague, Czech Republic, and Marek Sikorski, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznań, Poland, have developed an efficient one-pot, three-component method using readily available substrates, providing a novel and effective route to functionalized 5-aryldeazaalloxazines (5-arylpyrimido[4,5-b]quinoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones; pictured). The reaction uses readily available reagents and starts with N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid, an aromatic aldehyde, and aniline. Subsequent purification is not needed.
The reaction performed best in DMSO at 130°C. Bulky aldehydes like mesitaldehyde did not yield 5-aryldeazaalloxazine but instead formed 5-deazaalloxazine, with DMSO serving as a methylene source. The introduction of a strong methoxy group at position 7 of the 5-aryldeazaalloxazine core led to a bathochromic shift in the absorption spectra of the synthesized molecules, making them more suitable for visible light photocatalysis.
The researchers say that thier method significantly improves existing approaches by offering a direct route to the introduction of an aryl moiety into the C(5)-position of deazaalloxazines and opens a new route to the synthesis of powerful, photoredox, flavin-like catalysts, as well as potent, biologically active compounds.
- A facile three-component route to powerful 5-aryldeazaalloxazine photocatalysts,
Ivana Weisheitelová, Radek Cibulka, Marek Sikorski, Tetiana Pavlovska,
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1831–1838.
https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.20.161