Energy conversion and storage via the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) could be used to provide energy where and when it is needed. Reversible electrochemical devices operate either as an electrolyzer to generate H2 and O2 from water, or as a fuel cell, combining H2 and O2 to produce water and electricity. Unfortunately, the cathode reaction is sluggish and requires effective catalysts. Platinum and iridium are the most active catalysts for ORR and OER, respectively, but their low abundance makes any commercial use difficult.
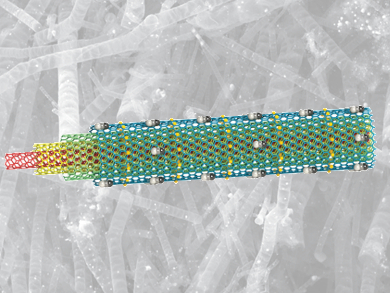
Shiv Gupta, University at Buffalo, New York, USA, and colleagues have engineered a new class of bifunctional electrocatalysts. They consist of ultra-large nitrogen-doped graphene tubes with a diameter of over 500 nm, and are decorated with FeCoNi alloy particles. These tubes are formed from dicyanamide as a carbon source, nitrogen, and Fe/Co/Ni acetate as the source of the transition metal in a low-cost graphitization process.
The resulting tubes are electrochemically durable in alkaline media and capable of catalyzing both the OER and the ORR reaction. The catalytic activity of the material is comparable to the activity of platinum.
- Highly Active and Stable Graphene Tubes Decorated with FeCoNi Alloy Nanoparticles via a Template-Free Graphitization for Bifunctional Oxygen Reduction and Evolution,
Shiva Gupta, Liang Qiao, Shuai Zhao, Hui Xu, Ye Lin, Surya V. Devaguptapu, Xianliang Wang, Mark T. Swihart, Gang Wu,
Adv. Energy Mater. 2016.
DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201601198