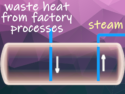
Currently, China is the world’s largest greenhouse-gas emitter. On March 16, it has approved its 13th Five-Year Plan. According to this economic development strategy, the country wants to reduce energy use and air pollution, and wants to expand on energy sources such as wind, solar and nuclear. This led specialists to assume that Chinese emissions are already nearing their peak well ahead of schedule.
The five-year plan includes the goal to reduce carbon intensity (carbon dioxide emitted per unit of gross domestic product) by 18 %. The 2011 five-year plan set a 17 % target. The total energy consumption is limited for the first time: by 2020 China should consume not more energy equivalent to 5 billion tonnes of coal. In 2015 consumed energy was equivalent to 4.3 billion tonnes. Detailed plans on how to achieve these commitments are expected to be released in the coming months.
China is on track to achieve its previous targets and leads the world in the deployment of renewable energy. In 2015, it invested some US$110 billion on renewable energy, twice as much as the United States, according to the World Resources Institute (WRI).
- China’s carbon emissions could peak sooner than forecast,
Jeff Tollefson,
Nature 2016, 531, 425
DOI: 10.1038/531425a