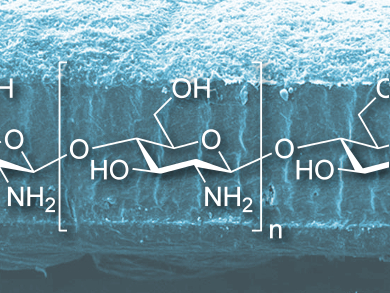
Biopolymers can be used as sustainable and functional films for medical applications and food packaging. Their mechanical, optical, and chemical properties need to be tailored to the respective application. Chitosan, the N-deacetylation product of chitin (found, e.g., in the shell of shrimps), has promising characteristics such as antimicrobial activity and optical transparency. It does, however have drawbacks, namely poor thermal and UV stability.
Abdolreza Simchi and colleagues, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, have developed flexible, transparent, and antimicrobial films by combining chitosan with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets. The films were prepared by combining solutions of chitosan and PVP with a suspension of the GO nanosheets and slowly evaporating the solvent in Petri dishes over a period of 48 hours.
The resulting films contained up to 50 vol% PVP and 1–3 % GO by weight. The optical properties could be tuned, more PVP made the films more transparent. The films showed improved thermal stability over pure chitosan, as well as high water permeabilty. The antimicrobial effect was tested with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, and the film showed high antibacterial capacity, caused by the chitosan and graphene oxide components.
- Physicochemical and antibacterial properties of chitosan-polyvinylpyrrolidone films containing self-organized graphene oxide nanolayers,
Nafiseh Mahmoudi, Fatemeh Ostadhossein, Abdolreza Simchi,
J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/app.43194