A notable click reaction is the copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC). It was originated by Sharpless and Meldal in 2001. The regioselective and high-yield 1,2,3-triazole is obtained in the presence of Cu(I) catalyst under the benign reaction conditions.
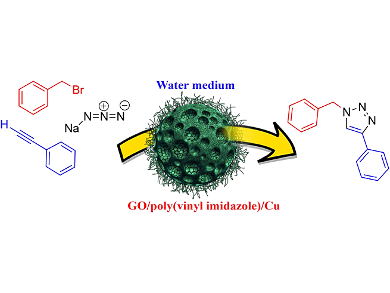
Ali Pourjavadi, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, and colleagues synthesized a heterogeneous polymeric catalyst by immobilization of copper ions in a graphene oxide (GO)/poly(vinyl imidazole) nanocomposite. The catalyst was proven to be highly active in a practical protocol for click synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole via one-pot three-component cycloaddition of halides, terminal alkynes, and sodium azide. The reaction was carried out in water and good to excellent yields of products were obtained using only 1.0 mol % of catalyst. The catalyst can be readily recovered and reused eight times without significant loss of activity.
In this catalytic system, GO is entrapped into a cross-linked poly(vinyl imidazole) matrix. Then copper is adsorbed onto the nanocomposite support by complexation with the imidazole rings in the polymer chains. The multi-layered nature of the cross-linked polymer increases the copper loading onto the catalyst.
- Graphene oxide/poly(vinyl imidazole) nanocomposite: an effective support for preparation of highly loaded heterogeneous copper catalyst,
Ali Pourjavadia, Niloofar Safaiea, Seyed Hassan Hosseinia and Craig Bennettb,
Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015.
DOI 10.1002/aoc.3336