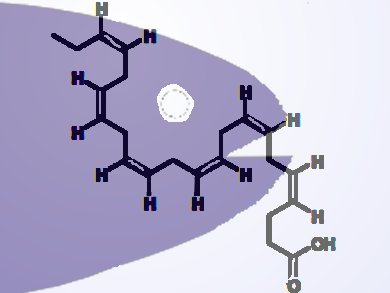
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; pictured) is an omega-3 fatty acid abundant in cold-water oceanic fish oils. It is believed to be a health dietary component as it reduces the levels of blood triglycerides and thus the risk of heart diseases.
According to Michael Collins, Loyola University Chicago, IL, USA, and colleagues, DHA may also protect alcoholic patients from ethanol-dependent brain damage. The researchers cultivated rat brain cells in vitro and exposed them to elevated concentrations of alcohol either in the presence or in the absence of DHA. Whereas cells exposed only to alcohol underwent massive inflammatory processes and ultimately died, these phenomena were markedly reduced when the cells were concomitantly exposed to DHA. DHA anti-oxidant properties most likely account for these protective effects.
Cold-water oceanic fish oils may, therefore, prevent neuronal degeneration in alcohol abusers.
- Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Adult Rat Brain from Binge Ethanol Exposure: Abrogation by Docosahexaenoic Acid,
Vinod K. Yaragudri, Nuzhath Tajuddin, Kwan-Hoon Moon, S. Alex Marshall, Kimberly Nixon, Edward J. Neafsey, Hee-Yong Kim, Michael A. Collins,
PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101223.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101223