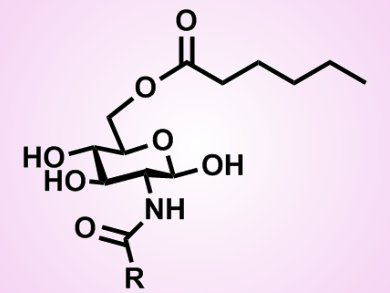
Glycolipids are fatty acid sugar esters. Their amphiphilic and non-ionic character results in highly emulsifying, stabilizing, and detergent properties. Furthermore glycolipids are non-toxic, taste- and odorless and completely biodegradable. Therefore, they are used for many different applications, ranging from food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and cleaning products. Glycolipids can be synthesized by enzyme-catalyzed reactions in organic solvents. The limiting factor here is the low solubility of sugars in non-polar organic solvents, in which lipases exhibit esterification activity.
Martin Pöhnlein, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), Germany, and colleagues synthesized two novel glycolipids (2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-6-O-hexanoate-D-glucose and 2-(butyrylamino)-2-deoxy-6-O-hexanoate-D-glucose) with N-acetyl-glucosamin (GlcNAc) and N-butyryl-glucosamin (GlcNBu) as sugar moieties with commercially available lipases.
HPLC analysis shows that the hydrophobicity of the sugar has a major impact on the reaction and that prior dissolving of the sugars in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) enhances the reaction rate and the yield of the synthesis even further.
This approach widens the possibilities for the synthesis of novel glycolipids with tailor-made properties for various applications.
- Enzymatic synthesis of amino sugar fatty acid esters,
Martin Pöhnlein, Christin Slomka, Olga Kukharenko, Tobias Gärtner, Lars O. Wiemann, Volker Sieber, Christoph Syldatk, Rudolf Hausmann,
Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/ejlt.201300380