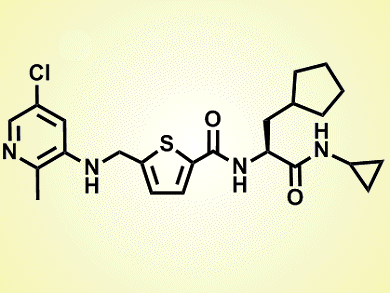
The serine/threonine phosphatase Wip1 plays an important role in tumor development. Despite its aberrant activity characterizing different forms of cancer, selective inhibitors are still lacking. By performing two high-throughput screens, Rakesh Kumar and co-workers, GlaxoSmithKline, USA, discovered a novel compound that blocks Wip1 activity through an allosteric mechanism.
The novel molecule, GSK2830371 (pictured), acts by binding to a flap subdomain that regulates Wip1’s enzymatic activity and substrate recognition. As this domain is not present in other phosphatases, its binding to GSK2830371 results in a selective and potent inhibition of Wip1. As a consequence, when GSK2830371 was tested in animal models suffering from a blood cancer (lymphoma), it effectively blocked the tumoral growth.
GSK2830371 thus holds promise as a novel anticancer drug.
- Allosteric Wip1 phosphatase inhibition through flap-subdomain interaction,
Aidan G Gilmartin, Thomas H Faitg, Mark Richter, Arthur Groy, Mark A Seefeld, Michael G Darcy, Xin Peng, Kelly Federowicz, Jingsong Yang, Shu-Yun Zhang, Elisabeth Minthorn, Jon-Paul Jaworski, Michael Schaber, Stan Martens, Dean E McNulty, Robert H Sinnamon, Hong Zhang, Robert B Kirkpatrick, Neysa Nevins, Guanglei Cui, Beth Pietrak, Elsie Diaz, Amber Jones, Martin Brandt, Benjamin Schwartz, Dirk A Heerding, Rakesh Kumar,
Nature Chemic. Biol. 2014.
DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1427