The androgen receptor determines and maintains male features. However, when mutated, it causes the death of spinal cord and brainstem’s motor neurons, promoting a neurodegenerative disease known as spinal and bulbar muscolar atrophy (SBMA). Traditional therapeutic strategies based on androgen withdrawal have shown limited efficacy. Thus, alternatives are needed.
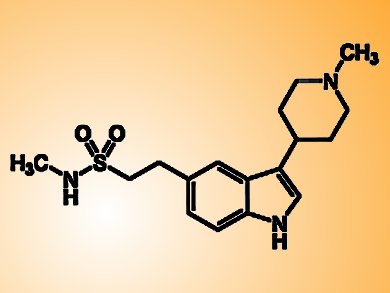
According to Makoto Minamiyama, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan, and colleagues naratriptan, a serotonin receptor agonist widely used to treat migraine, is effective against the disease. The scientists discovered that this compound targets calcitonin-gene related peptide A, a molecule which mediates androgen receptor’s neurotoxic effects. As a consequence, naratriptan ameliorated the neurodegenerative symptoms in a mouse model of SBMA.
- Naratriptan mitigates CGRP1-associated motor neuron degeneration caused by an expanded polyglutamine repeat tract,
M. Minamiyama, M. Katsuno, H. Adachi, H. Doi, N. Kondo, M. Iida, S. Ishigaki, Y. Fujioka, S. Matsumoto, Y. Miyazaki, F. Tanaka, H. Kurihara, G. Sobue,
Nat. Med. 2012, 18 (10), 1531-1538.
DOI: 10.1038/nm.2932