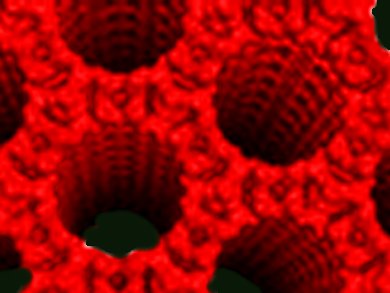
The binding energy of an electron in a material determines its chemical and physical properties. For metal−organic frameworks (MOFs) binding energies are unknown.
Keith T. Butler, Christopher H. Hendon, and Aron Walsh, University of Bath, UK, use computational chemistry to determine values for the binding of electrons in porous frameworks. They access a vacuum potential level at the center of the pores. With this approach, they determine the electron removal energies for six archetypal MOFs including zeolitic, covalent and ionic frameworks. These electron removal energies explain the physical origin of conductivity (COF-1M) and photocatalyic behavior (MIL-125).
According to the researchers, knowledge of the electronic chemical potentials provides a roadmap for tuning the performance of photo- and electro-active frameworks.
- Electronic Chemical Potentials of Porous Metal−Organic Frameworks,
Keith T. Butler, Christopher H. Hendon, Aron Walsh,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014.
DOI: 10.1021/ja4110073