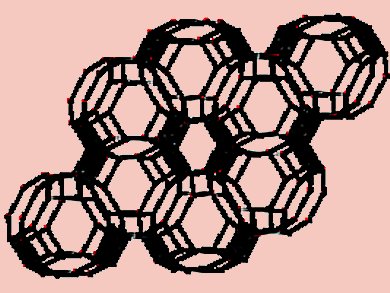
Jianhua Yang, Dalian University of Technology, Liaoning, China, and colleagues propose a new seeding method, namely, varying-temperature hot-dip coating (VTHDC), for synthesis of zeolite T membranes by secondary hydrothermal growth on coarse macroporous alumina supports. Zeolite T is a synthetic analog of the natural-occurring zeolite-erionite.
The VTHDC seeding method is based on a pressure difference resulting from the rapid temperature drop. The method is composed of hot-dip coating at higher temperature 448 K, rubbing off the superfluous crystals, and hot-dip coating at lower temperature. It is found flexible and effective for combined control of the seed suspension concentration, seeding temperature, and seed size. By the method, a combined seed layer manipulation including the seed size, coverage, thickness, and defect and surface roughness can be realized.
A thin continuous, smooth defect-free asymmetric seed layer of zeolite T was achieved consisting of large and small seed crystals of 2 and 0.4 µm, respectively. The large seeds mainly act as filler to reduce the pore size and surface roughness of the support, whereas the small seeds serve to provide nucleation sites for the growth of T crystals. The resulting zeolite T membrane M5 showed a total flux of 2.12 kg/m2h and S.F. of 1301 for 90 wt % EtOH aqueous solution at 348 K.
- High-Performance Zeolite T Membrane for Dehydration of Organics by a New Varying Temperature Hot-Dip Coating Method,
Xiaoxia Chen, Jinqu Wang, Dehong Yin, Jianhua Yang, Jinming Lu, Yan Zhang, Zan Chen,
AIChE J. 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/aic.13851