Erytropoietin (EPO) is a protein which stimulates the production of red blood cells. As a consequence, it is used to treat anemia, a pathological loss of red cells occurring in patients affected by cancer or undergoing chemotherapy. Since the chemical synthesis of this molecule is very challenging, EPO is currently produced through biological techniques (recombinant DNA technology).
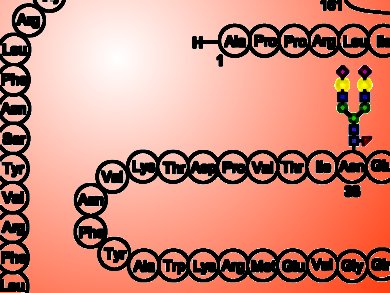
Samuel J. Danishefsky, Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research, New York, NY, USA, and colleagues developed a protocol to produce EPO via total chemical synthesis. The researchers assembled EPO by connecting together five separate synthetic peptides. To achieve this task, they used a procedure known as native chemical ligation, namely a reaction which joins together unprotected polypeptide chains. Moreover, since EPO activity and stability depends on the presence of four complex sugar chains (glycans), before ligating together the peptides, the scientists attached to them three N-linked glycans and a O-linked glycan moieties.
Using this strategy, the researches produced a fully synthetic EPO which exhibited an activity comparable to the one displayed by Procrit, a EPO formulation used in the clinic and produced through recombinant DNA technology
- Erythropoietin Derived by Chemical Synthesis,
P. Wang, S. Dong, J.-H. Shieh, E. Peguero, R. Hendrickson, M. A. S. Moore, S. J. Danishefsky,
Science 2013, 342, 1357–1360.
DOI: 10.1126/science.1245095



best wine production mechanism