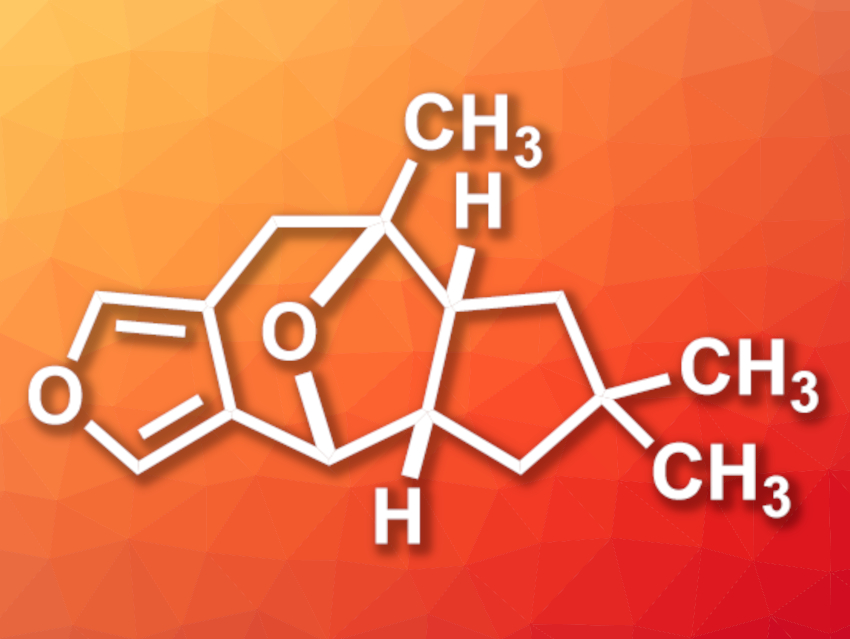
Furanether A (pictured) is a tetracyclic natural product with a 1-methyl-8-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane core and four contiguous stereocenters. It was first isolated from the mushroom Russula sardonia and has shown antifeedant activity, which means it can prevent animals from feeding on plants.
Dao-Yong Zhu, Shao-Hua Wang, Lanzhou University, China, and colleagues have performed the first total synthesis of (±)-furanether A. The team started from ethyl 2-oxopropanoate and a simple enone, which were combined using a [4+2] cycloaddition. The resulting intermediate was functionalized and subjected to a cyclization to form the furan unit, followed by the installation of a Weinreb amide. A Shapiro reaction was used to install the second five-membered ring of the target compound. The 1-methyl-8-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane core was then constructed using a C–H oxidation/oxa-[3,3] Cope rearrangement/aldol cyclization sequence. After the removal of a formaldehyde group, the desired (±)-furanether A was obtained.
(±)-Furanether A was synthesized in 13 linear steps and 0.85 % overall yield. According to the researchers, the work could allow biological activity studies of furanether A, as well as the synthesis of other bioactive natural products containing an 8-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane core.
- Total Synthesis of (±)-Furanether A,
Da-Ping Jin, Zhu-Peng Gao, Lin Liu, Shi-Qi Cao, Xue-Tao Xu, Xue-Wei Hou, Tian-Lu Zheng, Li-Ming Jiang, Dao-Yong Zhu, Shao-Hua Wang,
Org. Lett. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03353