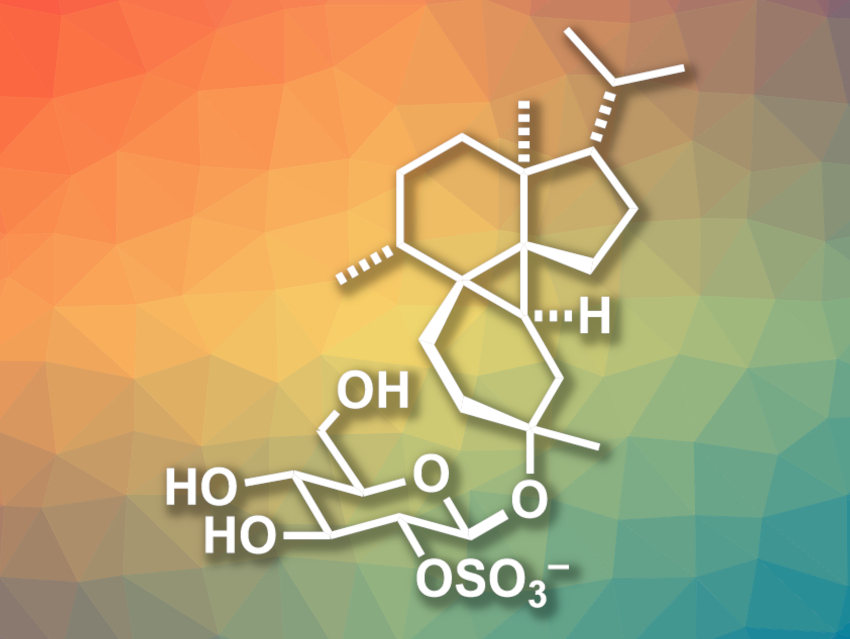
Marine-derived natural products often have interesting, complex structures and potentially useful biological activities. Peyssonnoside A (pictured), for example, has been isolated from the red alga Peyssonnelia sp. and has been found to show activity against a type of malaria parasite and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The compound features a tetracyclic 5/6/3/6 carbon framework with a highly substituted cyclopropane ring.
Gleb A. Chesnokov and Karl Gademann, University of Zurich, Switzerland, have performed the first total synthesis of peyssonnoside A. The team first prepared two precursors via known routes: one from 2-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one in one step and one from γ-valerolactone in three steps. They were reacted in a Mukaiyama-type Michael addition which was followed by a Robinson annulation to form the A and B rings. The three-ring was then constructed using a Simmons–Smith cyclopropanation. Additional sidechains were installed and the final six-ring was closed via a ring-closing metathesis reaction. An anaerobic Mukaiyama hydration was then used to stereoselectively install the OH group.
In summary, the non-sugar fragment of peyssonnoside A, peyssonnosol, was prepared in 15 steps and 21 % overall yield. This intermediate can then be glucosylated and the sulfate group introduced to obtain the desired peyssonnoside A.
- Concise Total Synthesis of Peyssonnoside A,
Gleb A. Chesnokov, Karl Gademann,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c07135