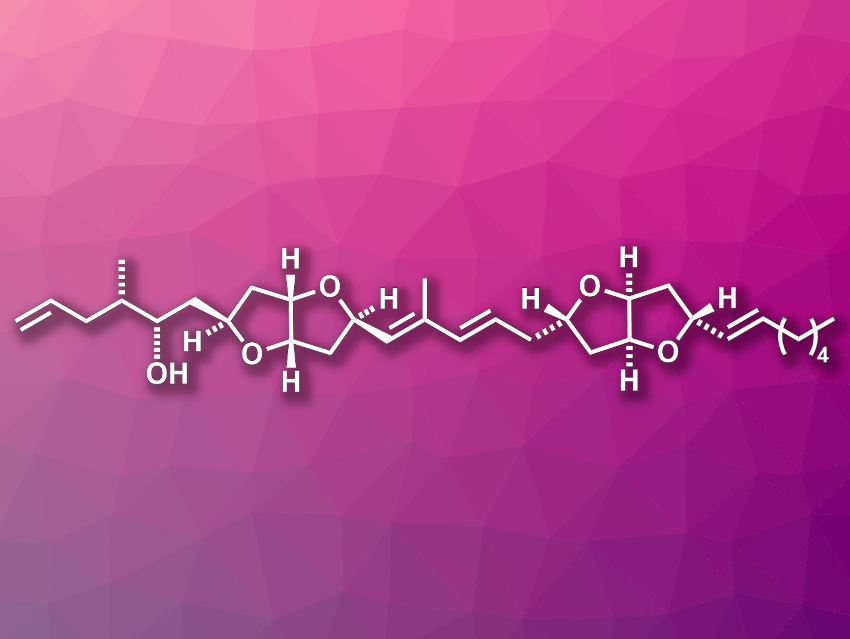
Amphirionin-2 (pictured) is a polyketide natural product that was first isolated from the marine dinoflagellates Amphidinium sp. The compound has shown promising in vitro anticancer activities against, e.g., certain human colon cancer and lung cancer cell lines. It features two hexahydrofuro[3,2-b] furan units and ten stereogenic centers.
Rajib Kumar Goswami, Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science, Jadavpur, Kolkata, India, and colleagues have developed a convergent route for the asymmetric total synthesis of amphirionin-2. The team started from aspartic acid and glycidyl benzyl ether, which were converted to an unsaturated diol. Then they used a Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation followed by a cycloetherification to build the fused-ring systems. A Wittig olefination, a Crimmins propionate aldol reaction, and a Julia–Kocienski olefination were key steps in the functionalization of the building blocks. Finally, another Julia–Kocienski olefination was used to connect the resulting two large segments of the desired compound, each containing one of the two fused-ring systems.
Amphirionin-2 was obtained in 30 longest linear steps from aspartic acid in 0.3 % overall yield. The team also prepared two other stereoisomers that had previously been proposed as the structure of the natural product. The characterization data of the three compounds provided further evidence to confirm the correct structural assignment of amphirionin-2.
- Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Amphirionin-2,
Dhiman Saha, Gour Hari Mandal, Rajib Kumar Goswami,
J. Org. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c00686