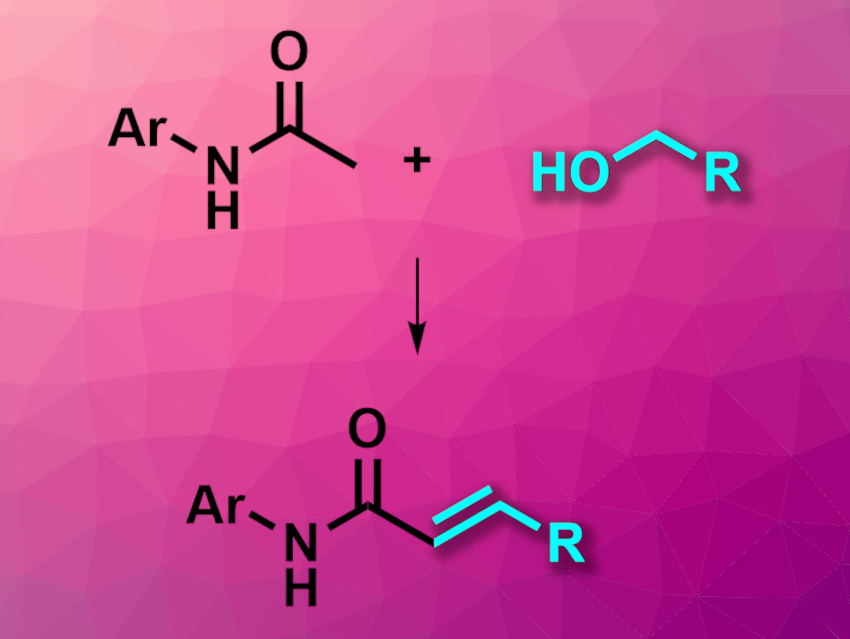
Alkenylation reactions are useful in organic synthesis. Existing methods for intermolecular alkenylations often require prefunctionalization and/or harmful reagents. Amides can be unsuitable as substrates in these reactions, but α,β-unsaturated amides are useful products. These compounds are usually synthesized from α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids and amines, which creates waste and is hampered by the limited availability of suitable carboxylic acids.
Biplab Keshari Pandia and Chidambaram Gunanathan, National Institute of Science Education and Research (NISER), Homi Bhabha National Institute, Bhubaneswar, India, have developed a manganese-catalyzed direct α-alkenylation of amides using alcohols (pictured). The team used a variety of N-arylamides and benzyl alcohol derivatives as substrates, an Mg(I) pincer complex as the catalyst, NaOtBu as a base, and tert-amyl alcohol as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 135 °C.
The team obtained the desired α,β-unsaturated amides in moderate to good yields. The reaction produces only water and H2 as byproducts, can use renewable biobased alcohols, and relies on earth-abundant manganese for its catalyst, which makes it interesting for green and sustainable chemistry.
- Manganese(I) Catalyzed α-Alkenylation of Amides Using Alcohols with Liberation of Hydrogen and Water,
Biplab Keshari Pandia, Chidambaram Gunanathan,
J. Org. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c00685

![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)