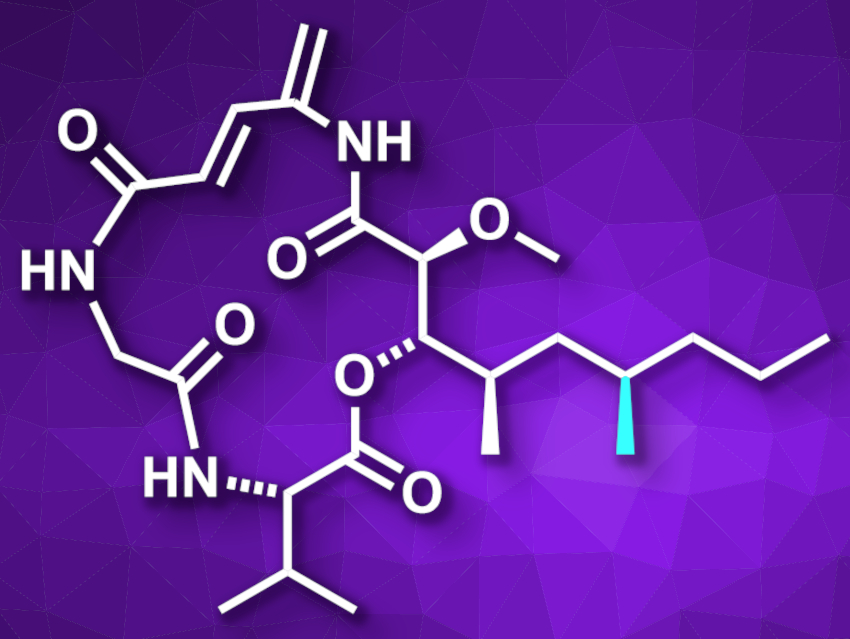
Boholamide A (pictured) is a macrocyclic depsipeptide with a 15-membered ring and was originally isolated from a mollusk. The compound has a 4-amino-2,4-pentadienolate (APD) unit (pictured top left), which is also found in several other natural products that show anti-cancer activities. However, the isolated amounts of boholamide A were too small for a comprehensive evaluation of its biological activities.
Yue Chen, Quan Zhang, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, and colleagues have performed the first total synthesis of boholamide A as well as its previously proposed structure, which is an epimer of the compound with a different configuration at C6 (pictured in light blue). The team used a convergent route starting from camphorsultam derivatives, an L-serine derivative, and Boc-L-valine. The resulting components were connected using a Mukaiyama aldol reaction, an ester coupling, and a peptide coupling. The macrolactamization step to close the 15-membered ring was performed on a gram scale. Based on NMR spectroscopic data, the team tentatively revised the chiral center at C6 to be 6R instead of the previously proposed 6S.
The researchers obtained both boholamide A and its previously proposed structure in 16 longest linear steps and in 5.46 % and 2.80 % overall yield, respectively. The work could allow further investigations of the anticancer properties of boholamide A.
- Total Synthesis and Structure Revision of Boholamide A,
Fangzhi Han, Guangju Liu, Xuhai Zhang, Yahui Ding, Liang Wang, Yijing Wu, Yue Chen, Quan Zhang,
Org. Lett. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01382