Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are porous crystalline networks made from organic building blocks. They can be useful, e.g., for the adsorption of pollutants. However, COFs are usually produced in powder form and can be difficult to process.
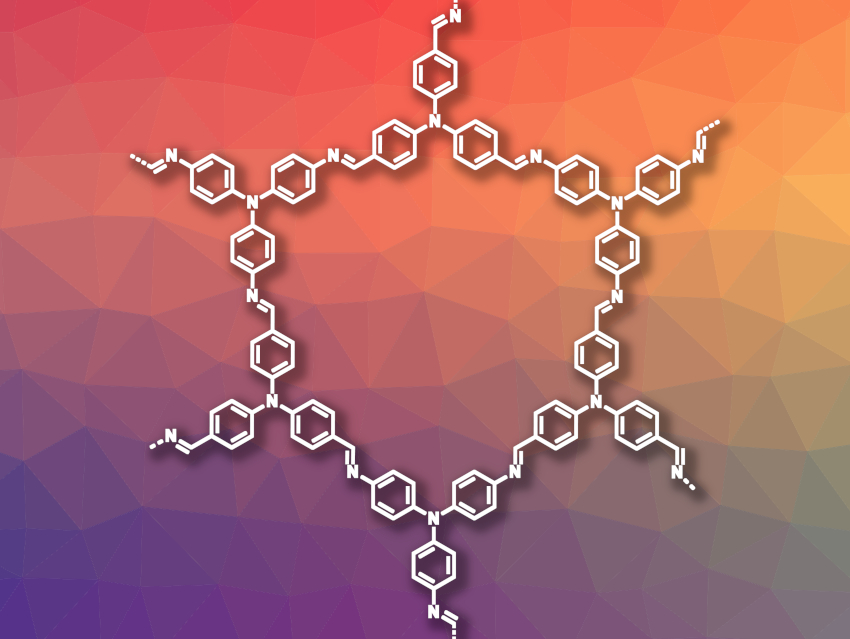
Rafael Verduzco, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, and colleagues have developed a simple method for making macroscopic, crystalline, imine-based COF gels and aerogels. The team prepared six different imine COFs (example pictured) by dissolving the corresponding amine and aldehyde monomers in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and adding acetic acid as the catalyst to form a gel in which the COF formation takes place. Then, the gel was washed in tetrahydrofuran (THF), acetone, and ethanol. Finally, the gel was dried under supercritical CO2 to obtain an aerogel. For some monomers, an additional reactivation in a mixture of dioxane and mesitylene and a second drying step were needed to obtain the desired crystalline aerogels.
The resulting COF aerogels have porosities and crystallinities comparable to conventionally synthesized COF powders. The team used them, e.g., for the absorption of organic solvents such as chloroform, the adsorption of organic dyes such as methylene blue, and the adsorption of iodine. They observed excellent performance for these applications. In addition, the aerogels can be easily recovered and reused, for example, after organic solvent absorption or organic dye adsorption.
- Pure Crystalline Covalent Organic Framework Aerogels,
Dongyang Zhu, Yifan Zhu, Qianqian Yan, Morgan Barnes, Fangxin Liu, Pingfeng Yu, Chia-Ping Tseng, Nicholas Tjahjono, Po-Chun Huang, Muhammad M. Rahman, Eilaf Egap, Pulickel M. Ajayan, Rafael Verduzco,
Chem. Mater. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c01122
![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)

