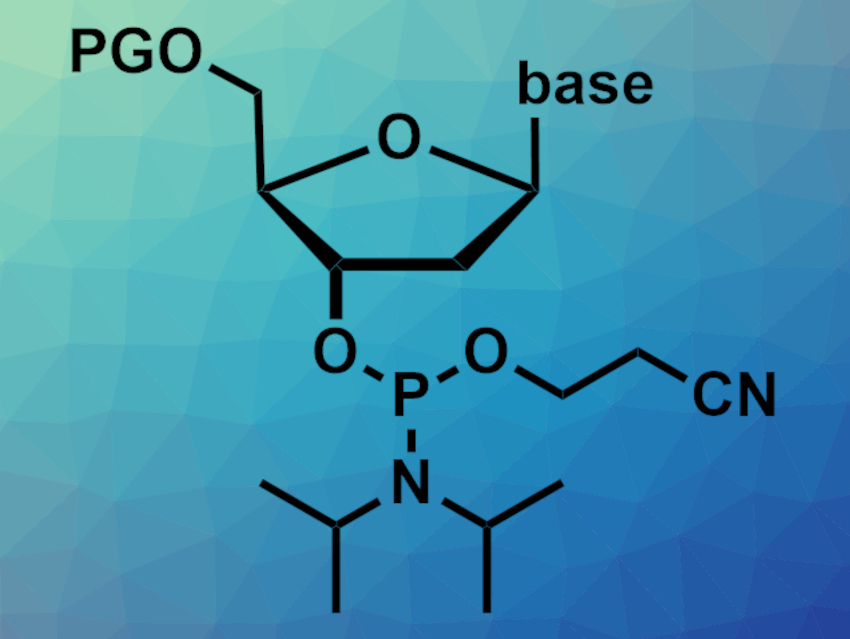
Nucleoside phosphoramidites (example pictured, PG = protecting group) are nucleoside derivatives. They can be used as building blocks to prepare oligonucleotides with any desired sequence via chemical synthesis in an automated process. Phosphoramidites should ideally be stored under an inert atmosphere and below –20 °C. Automated oligonucleotide synthesizers, however, work at ambient temperature, leading to degradation of the phosphoramidite precursors. Preparing phosphoramidites in situ could solve this problem.
Kurt V. Gothelf, Aarhus University, Denmark, and colleagues have developed an on-demand flow synthesis of phosphoramidites from their corresponding alcohols. This process avoids both the manual synthesis of these precursors, which can take up to twelve hours, as well as the need to store phosphoramidites. The team flushed the substrates through a functionalized resin—a setup that could be fully integrated into an automated oligonucleotide synthesis. In the resin, the substrates are rapidly converted to phosphoramidites.
The team used an (aminomethyl)polystyrene (AM-PS) resin, which was functionalized with nitrotriazole as an activator and loaded with 2-cyanoethyl diisopropylchlorophosphoramidite (PCl) as a reagent. 9-Azajulolidine was used as an additive for the transfer of the resin-bound reagent to the alcohols. Using this approach in a flow setup, the researchers prepared both nucleoside and non-nucleoside phosphoramidites from the respective alcohols in near-quantitative yields within minutes. The nucleoside phosphoramidites could be used directly in automated oligonucleotide synthesis without purification.
- On-demand synthesis of phosphoramidites,
Alexander F. Sandahl, Thuy J. D. Nguyen, Rikke A. Hansen, Martin B. Johansen, Troels Skrydstrup, Kurt V. Gothelf,
Nat. Commun. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22945-z