The EnXylaScope project is funded by the European Commission with €6 million under the Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. It aims to discover novel enzymes for xylan debranching. The production systems for these enzymes will be optimized and the enzymes will be used to produce a debranched (water-insoluble) form of xylan that has properties that make it suitable as ingredients in a range of consumer products. The debranched xylan will be further modified using available enzymes to provide it with additional functionalities, thereby expanding the range of potential consumer products. Three types of enzymatically modified xylan will be produced and tested for six consumer products. These products will cover cosmetics, personal care, and nutraceuticals.
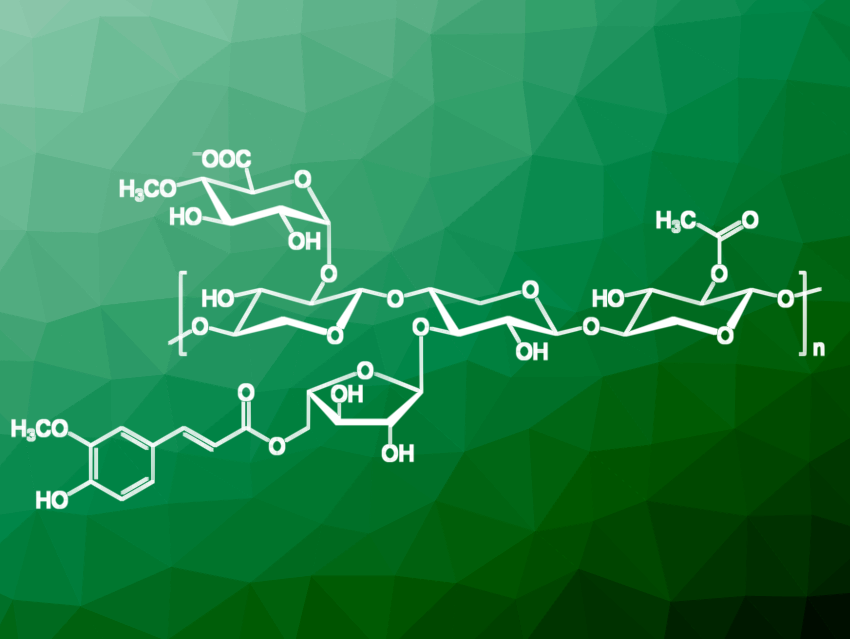
Xylans (pictured) are biopolymers with excellent physical and chemical properties and the most important representatives of hemicelluloses. The hemicelluloses are a component of the cell wall of plants. Because of different modification possibilities, xylans are not a clearly definable component. In nature, they are degraded by xylanases. However, because of the inhomogeneous structure, degradation is not carried out by one xylanase, but by an enzyme complex.
The project will run from May 2021 to April 2025, with the EnXylaScope consortium coordinated by the AITIIP Technology Center, Zaragoza, Spain. EnXylaScope officially kicked off on May 18, 2021, in an online meeting with the whole project consortium involving 13 organizations from 10 European countries: Fundación AITTIP (project coordinator and research institution from Spain), Celiginis (SME from Ireland), IFEU – Institut fur Energie (research institution from Germany), LOBA.cx (SME and project dissemination leader from Portugal), SEPPIC – Societé d’Exploitation de Produits pour les Industries Chimiques (Industry from France), divis intelligent solutions GmbH (SME from Germany), Rise Research Institute of Sweden (research institution from Sweden), Techniche Universiteit Delft (University from The Netherlands), SINTEF (research institution from Norway), Kerry Ingredients (Industry from Ireland), FERMEX (SME from Denmark), Lunds Universitet (University from Sweden), and METGEN (SME from Finland).
Also of Interest