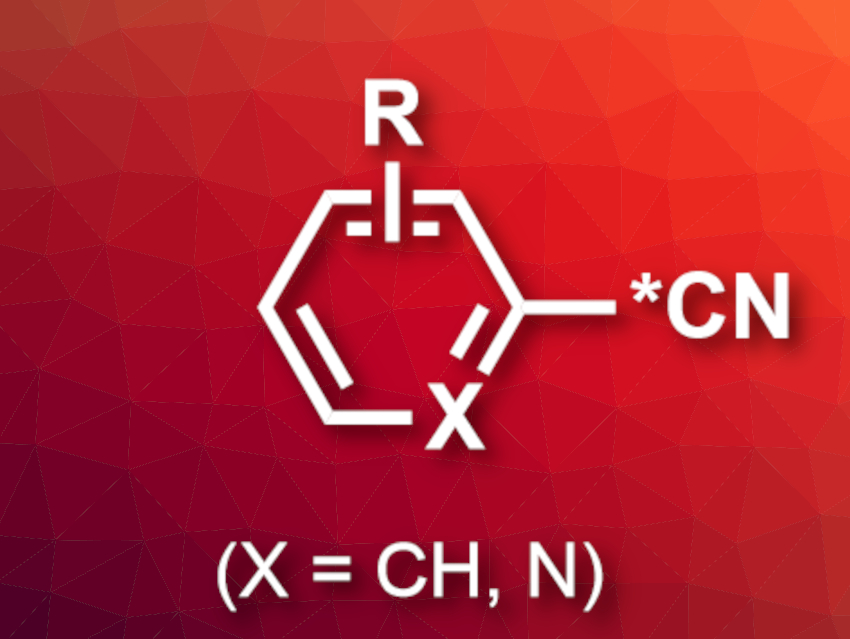
Radiolabeled pharmaceutically active compounds are useful in drug development. They can be used to trace the drugs and their metabolites. Carbon-14 (14C) is useful for these types of applications, as it provides a robust radiolabel—in contrast to tritium (3H), which can be exchanged quite easily. However, incorporating the radiolabel into the carbon skeleton of drugs can be challenging because there is a limited range of 14C-containing starting materials. It also produces larger amounts of radioactive waste. Introducing the radiolabel late in the synthesis would be preferable.
Sean W. Reilly, Neil A. Strotman, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and colleagues have developed a simple, late-stage, one-pot strategy for 13CN and 14CN exchange with the CN groups of aryl, heteroaryl, and alkenyl nitriles (example product pictured). The team used radiolabeled Ni(CN)2 as a reactant, Ni(COD)DQ (COD = 1,5‐cyclooctadiene, DQ = duroquinone) as a catalyst, PMe3 or PPh2Me as a ligand, BPh3 as a Lewis acid, and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as the solvent. The reactions were performed at 80 °C.
According to the team, this is the first carbon isotope exchange method for aryl, heteroaryl, and alkenyl nitriles that allows the late-stage incorporation of isotopic labels. It has a broad substrate scope and can be used for the labeling of complex drug-like molecules. As a proof of concept, the team converted the drug candidate belzutifan to the corresponding 14C-labeled tracer, with 52 % 14C incorporation and in 72 % isolated yield.
- Late-Stage Carbon Isotope Exchange of Aryl Nitriles through Ni-Catalyzed C–CN Bond Activation,
Sean W. Reilly, Yu-hong Lam, Sumei Ren, Neil A. Strotman,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c01454