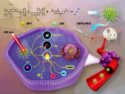
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines can prevent COVID-19, but they can also be used to treat or prevent other diseases, including some forms of cancer. Cancer immunotherapy vaccines can activate the immune system to attack tumors.
These vaccines contain mRNA that encodes proteins made specifically by tumor cells. When the mRNA enters antigen-presenting cells, they begin making the tumor protein and displaying it on their surfaces. This triggers other immune cells to seek and destroy tumors that also make this protein. However, mRNA is an unstable molecule and is quickly degraded by enzymes in the body. For cancer immunotherapy, researchers have tried using nanoparticles to protect and deliver mRNA, but these nanoparticles are typically cleared from the body within a few days after injection.
Guangjun Nie, Hai Wang, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, and colleagues have developed a hydrogel that, when injected under the skin, slowly releases mRNA nanoparticles, along with an adjuvant, i.e., a molecule that helps activate the immune system. The team used ovalbumin, a protein found in chicken egg whites, as a model antigen. They mixed ovalbumin mRNA and an adjuvant with graphene oxide (GO) and polyethylenimine (PEI) to form a hydrogel.
When injected under the skin of mice with melanoma tumors engineered to express ovalbumin, the hydrogel slowly released mRNA and adjuvant nanoparticles over a 30-day period. The mRNA vaccine activated antigen-specific T-cells and stimulated antibody production, causing tumors in the treated mice to shrink. The vaccine also prevented the formation of lung metastases. According to the researchers, these results demonstrate that the hydrogel has the potential to achieve long-lasting and efficient cancer immunotherapy with only a single treatment.
- In Situ Transforming RNA Nanovaccines from Polyethylenimine Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hydrogel for Durable Cancer Immunotherapy,
Yue Yin, Xiaoyang Li, Haixia Ma, Jie Zhang, Di Yu, Ruifang Zhao, Shengji Yu, Guangjun Nie, Hai Wang,
Nano Lett. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c05039