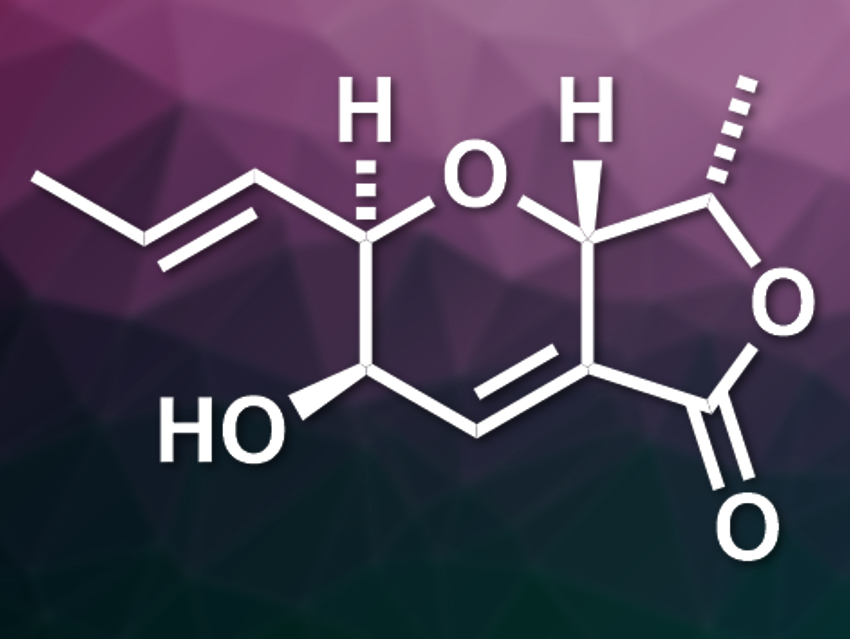
(−)-TAN-2483B (pictured) is a fungal metabolite. It has a furo[3,4-b]pyran-5-one framework and was discovered in fungal fermentation cultures together with its epimer (−)-TAN-2483A. TAN-2483A and mixtures of TAN-2483A and TAN-2483B have interesting bioactivities, but no bioactivity of pure (−)-TAN-2483B had been known so far.
Joanne E. Harvey, Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand, and colleagues have performed the first total synthesis of (−)-TAN-2483B. The team started from D-mannose, which was converted to a chloride-functionalized intermediate in two steps and then to a glycal. Cyclopropanation followed by in situ ring expansion and nucleophilic attack by an acetate anion then gave a glycosyl acetate. Alkynylation and deprotection steps led to a diol intermediate, which was subjected to oxidative cleavage to give an aldehyde, followed by a Julia–Kocienski reaction to introduce the propenyl side chain. The alkyne group was converted to a methyl ketone. A reduction of the ketone with sodium borohydride, a palladium-catalyzed carbonylative lactonization, and a final deprotection step then gave the desired (−)-TAN-2483B.
Overall, (−)-TAN-2483B was obtained in 14 steps from D-mannose. The team obtained a preliminary biological profile of (−)-TAN-2483B and found that the compound inhibits certain kinases and some bacterial pathogens, among other activities.
- Total Synthesis and Bioactivity Studies of Fungal Metabolite (−)-TAN-2483B,
Jordan A. J. McCone, Kalpani K. Somarathne, Christopher L. Orme, Russell J. Hewitt, Elysha-Rose Grant, Kelsi R. Hall, David F. Ackerley, Anne C. La Flamme, Joanne E. Harvey,
Org. Lett. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03303