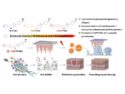
The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Coronaviruses such as this one have glycoprotein “spikes” on their surface. These spikes help SARS-CoV-2 enter host cells by binding to a receptor on the surface of the host cells’ membrane—the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Many COVID-19 patients lose their sense of smell, which suggests that the virus could target cells in the nose responsible for smell. However, the levels of ACE2 expression of these cells had not been known so far.
Andrew P. Lane, Mengfei Chen, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA, and colleagues have compared levels of ACE2 in different cell types and parts of the nose and upper airway. The team used tissue samples from the back of the nose of 23 patients, removed during endoscopic surgical procedures. They also studied biopsies from the trachea (windpipe) of seven patients. None of the patients had been diagnosed with coronavirus. The researchers used fluorescent dyes on the tissue samples to detect and visualize the presence of ACE2 under a microscope and compare its expression in different cells.
The researchers found by far the most ACE2 on the lining cells of the olfactory epithelium, the area at the back of the nose where the body detects smells. The levels of ACE2 in these cells was between 200 and 700 times higher than other tissue in the nose and trachea. This may explain the loss of smell that can be associated with a COVID-19 infection. It also suggests that these cells act as a reservoir for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. As a result, intranasal therapy might be a promising approach for COVID-19 treatment, the researchers suggest.
- Elevated ACE2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication,
Mengfei Chen, Wenjuan Shen, Nicholas R. Rowan, Heather Kulaga, Alexander Hillel, Murugappan Ramanathan, Andrew P. Lane,
Eur. Respir. J. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01948-2020
Also of Interest
 |
Clever Picture: Coronavirus Entering and Replicating in a Host Cell |
 |
Collection: SARS-CoV-2 Virus |