The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Certain enzymes, called viral proteases, are essential for the replication of the virus. SARS-Cov-2, in particular, relies on its main protease (Mpro/3CLpro) and the papain-like protease (PLpro). Papain-like proteases are not only important for virus replication, but can also act on proteins that regulate the host’s innate immune pathways, such as ubiquitin and interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15). This makes PLpro a promising target for COVID-19 drugs.
Ivan Dikic, Goethe University, Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, and Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology (IME), all Frankfurt am Main, Germany, and colleagues have investigated the biochemical, structural, and functional properties of the PLpro of the SARS-CoV-2 virus (SCoV2-PLpro) and compared them to those of the equivalent enzyme of the related SARS virus (SCoV-PLpro).
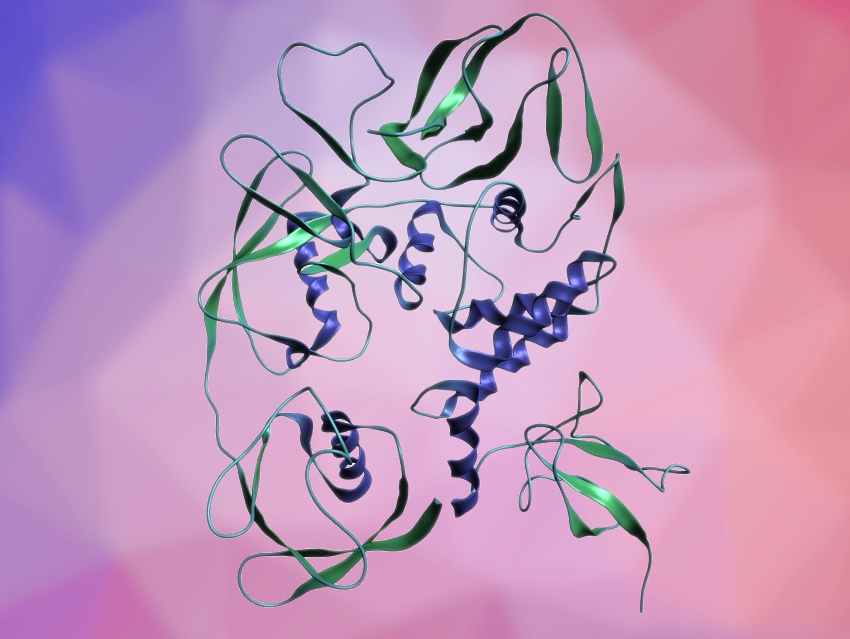
Using cell-culture-based experiments, the team found that the two enzymes have different substrate preferences. SCoV2-PLpro preferentially cleaves off the protein ISG15 from substrates and SCoV-PLpro predominantly targets ubiquitin chains. The team determined the crystal structure of a SCoV2-PLpro–ISG15 complex (pictured) and found certain protein residues that lead to a high affinity for ISG15 in SCoV2-PLpro. The resulting higher activity of SCoV2-PLpro for the cleavage of ISG15 leads to a greater inhibition of type I interferon production. Type I interferons are important for the activity of the immune system.
The team looked for inhibitors that could inhibit SCoV2-PLpro and tested GRL-0617, a naphthalene-based inhibitor originally developed against SCoV-PLpro. They found that GRL-0617 effectively blocked the enzyme, as well as overall SARS-CoV-2 virus replication. According to the researchers, such inhibitors of SCoV2-PLpro may lead to new COVID-19 drugs with a dual effect—blocking virus replication and promoting immunity in the host via an interferon pathway.
- Papain-like protease regulates SARS-CoV-2 viral spread and innate immunity,
Donghyuk Shin, Rukmini Mukherjee, Diana Grewe, Denisa Bojkova, Kheewoong Baek, Anshu Bhattacharya, Laura Schulz, Marek Widera, Ahmad Reza Mehdipour, Georg Tascher, Paul P. Geurink, Alexander Wilhelm, Gerbrand J. van der Heden van Noort, Huib Ovaa, Stefan Müller, Klaus-Peter Knobeloch, Krishnaraj Rajalingam, Brenda A. Schulman, Jindrich Cinatl, Gerhard Hummer, Sandra Ciesek, Ivan Dikic,
Nature 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2601-5
Also of Interest
- Collection: SARS-CoV-2 Virus
What we know about the new coronavirus and COVID-19 - LitCovid
Curated literature hub for tracking up-to-date scientific information about COVID-19 - Many publishers and other entities have signed a joint statement to ensure that COVID-19 research findings and data are shared rapidly and openly