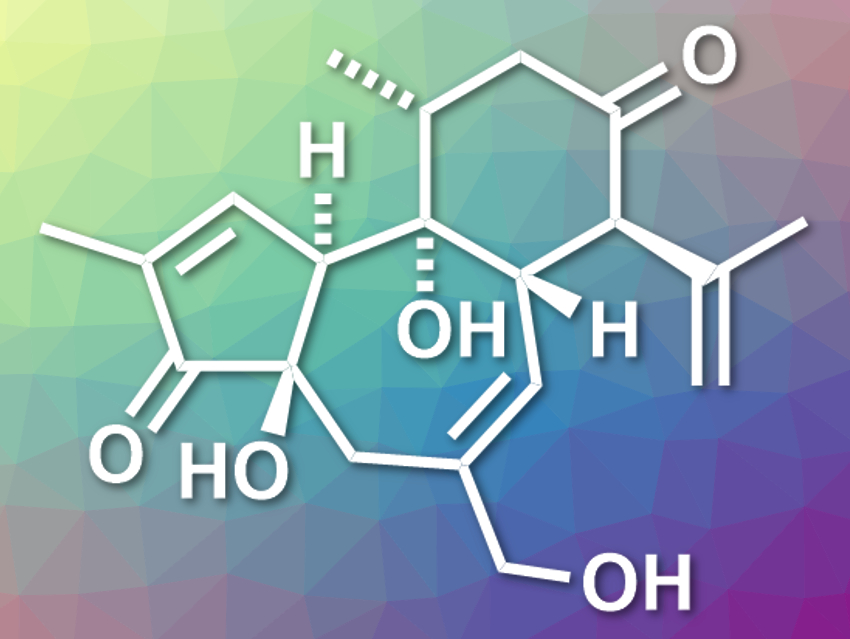
Crotophorbolone (pictured) is a diterpenoid natural product. It belongs to a family of diterpenoids that includes, for example, phorbol and prostratin. These compounds have interesting biological activities and tricyclic frameworks with multiple stereogenic centers. Crotophorbolone has a trans,trans-5/7/6 tricyclic ring system with six contiguous stereogenic centers, which is challenging to synthesize. The first total synthesis of crotophorbolone was achieved in 2015 [1] and required thirty-four linear steps.
Bo Liu and colleagues, Sichuan University, China, have performed an eighteen-step total synthesis of crotophorbolone using a convergent strategy. The team started from (−)-carvone and [+]dimethyl-2,3-O-isopropylidene-L-tartrate. Carvone was used as the basis for the six-membered ring and subjected to a diastereoselective hydroxylation and a vinylation. The tartrate was converted to the five-membered-ring fragment via a methallylation and an intramolecular aldol condensation.
The five-ring fragment was converted to an alkenyl lithium intermediate and coupled with the six-ring fragment in the presence of CeCl3. Ring-closing metathesis (RCM) was used to close the central seven-membered ring and give the desired 5/7/6 tricyclic skeleton. The synthesis was concluded by the selective introduction of hydroxyl groups to obtain crotophorbolone.
- Total synthesis of crotophorbolone,
Tianzi Yu, Ying Sun, Canhui Tu, Ting Chen, Shaomin Fu, Bo Liu,
Chem. Sci. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc02829k
Reference
- [1] Total Synthesis of Crotophorbolone,
Taro Asaba, Yuki Katoh, Daisuke Urabe, Masayuki Inoue,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14457–14461.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201509160


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)
