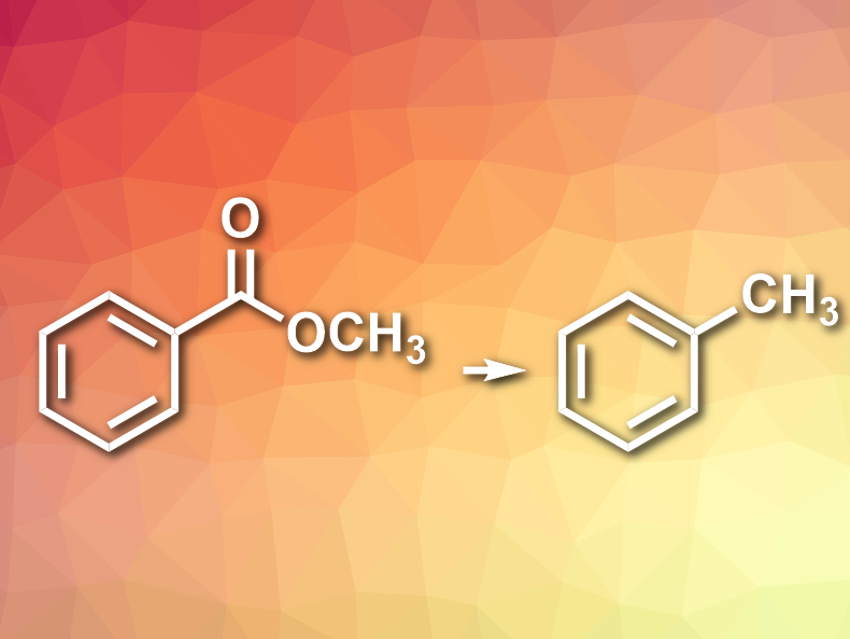
The reduction of carboxylic acids and their derivatives is a useful type of transformation in organic synthesis. Usually, the acids, esters, or amides are first reduced to the corresponding primary alcohol using harsh metal hydride reagents. The complete reduction then requires a second reaction to convert the primary alcohol to a methyl-substituted compound. Achieving the exhaustive reduction of carboxylic acid derivatives to methyl-substituted molecules in a single step is challenging.
Stephen G. Newman, University of Ottawa, ON, Canada, and colleagues have developed a one-step nickel-catalyzed method to reduce unactivated aryl esters directly to the corresponding methyl arenes (pictured). The team used Ni(cod)2 (cod = 1,5-cyclooctadiene) as a catalyst, together with a 1,3-dicyclohexyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligand, the organosilane 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane (TMDSO) as a reducing agent, KOtBu as a base, and toluene as the solvent. The aryl esters were converted to methyl arenes at 110 °C.
The desired products were obtained in good yields. According to the researchers, the reaction proceeds via an organosilane-mediated ester hydrosilylation, directly followed by Ni-catalyzed hydrogenolysis. The reaction is chemoselective and tolerates, e.g., benzyl ethers. A modified approach of this reaction can be used to create deuterated methyl groups (–CD3), which are useful for the study of reaction mechanisms.
- Exhaustive Reduction of Esters Enabled by Nickel Catalysis,
Adam Cook, Sekar Prakash, Yan-Long Zheng, Stephen G. Newman,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c02405